王金亮教授团队学术论文在SCIE二区期刊Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution上线发表
2023年12月15日,以马军(云南师范大学地理学部测绘工程专业2014级本科生)为第一作者,王金亮教授为通讯作者所撰写的题为“A landscape-based ecological hazard evaluation and characterization of influencing factors in Laos”的学术论文在SCI/SCIE二区期刊《Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution》上线发表(https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1276239).

研究景观生态危害的时空演变及人类和自然影响对于保护性管理和区域可持续发展至关重要。本研究应用景观格局分析方法和地理探测器对2000年、2010年和2020年的多源数据对老挝景观生态危害的变化和驱动因素进行分析。 结果表明:(1)老挝景观类型变化较为突出。森林面积减少,其他景观类型面积增加, 老挝的景观格局总体上发生了稳步变化。除人工地表景观指数发生明显变化外,其他景观指数保持稳定;(2)高、极端生态危害面积累计增加1947.81平方公里,低、较低生态危害面积累计减少8461.8平方公里,低和中生态危害地区占总面积的85%以上。生态危害低区主要分布在研究区西北和东南部,生态危害高发地区集中在中部和东北地区。研究期间老挝不同景观生态危害分布相似,总体呈现由北向南危害递减的规律; (3)获得了老挝景观生态危害的Moran’s I值。 虽然集聚效应很明显,但随着时间的推移,空间自相关性减弱。研究区景观生态危害的空间分布呈现显著的正自相关。高、低生态危害集聚区分别主要集中在东北部和东南部;(4)近20年来老挝景观生态危害时空演变可归因于自然和人为影响的相互作用。自然影响是老挝景观生态危害变化的重要驱动因素,其中年降水量和平均气温最为显着。人为影响,包括社会经济因素和区域可达性因素也严重影响了老挝当地的生态恶化。
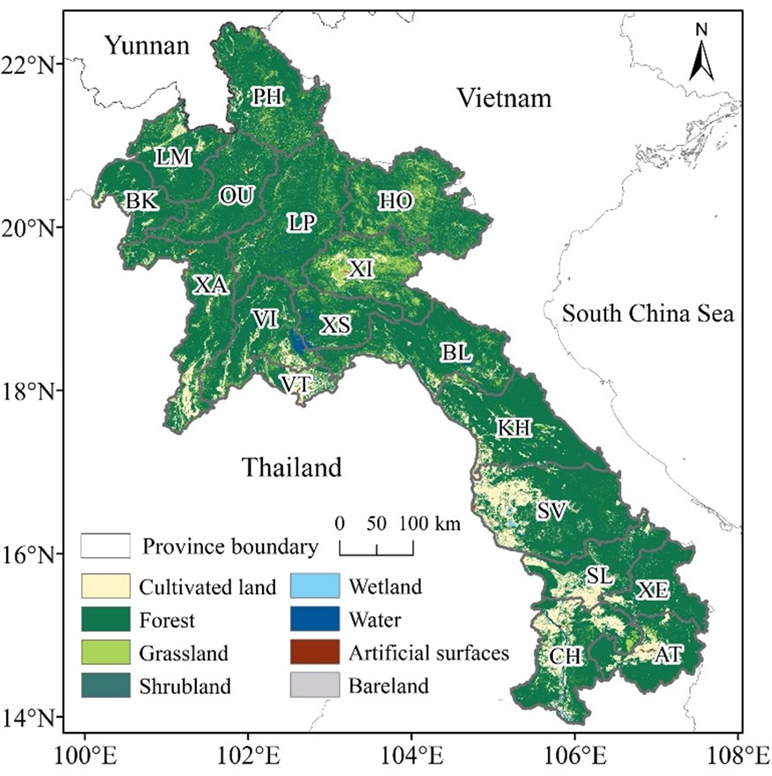
Fig. 1. Geographical location and land cover of Laos
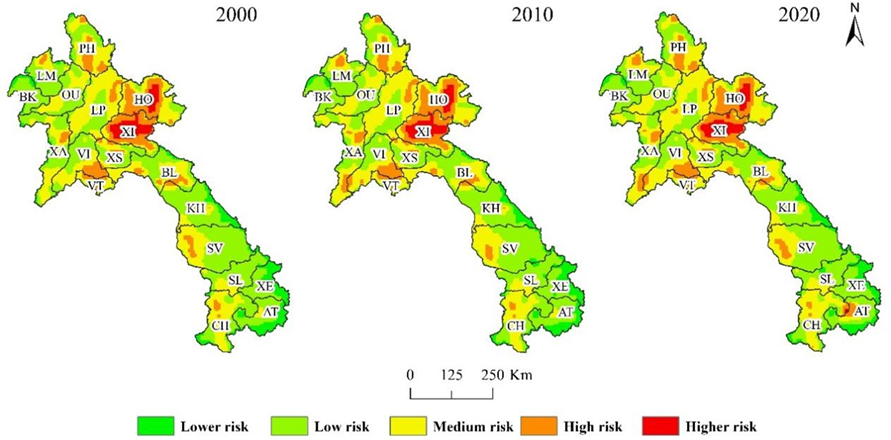
Fig. 2. Spatial distribution of landscape ecological hazard falling into various categories in Laos in 2000–2020.
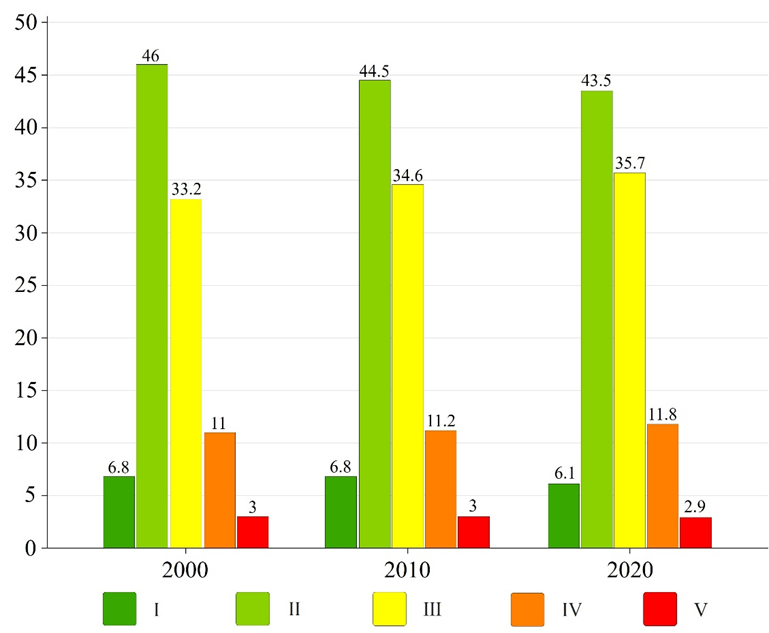
Fig. 3. Proportion of landscape ecological hazard classes in Laos, 2000–2020 (%).
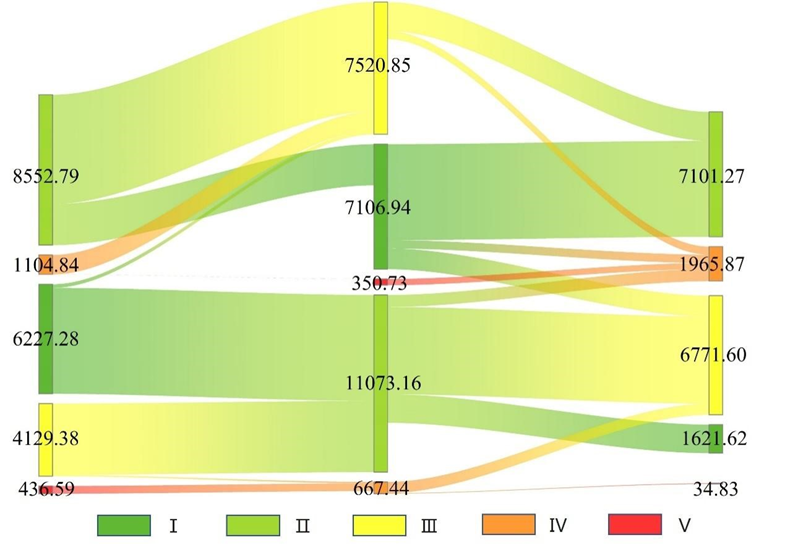
Fig. 4. Sankey diagram showing the transfer of landscape ecological hazard in Laos between 2000–2020 (km2).
该论文得到了王金亮教授主持的国家重点研发计划政府间国际科技创新合作重点专项:地理空间技术监测和评估土地利用/土地覆被变化对区域生态安全的影响(2018YFE0184300)、国家自然科学基金 (41961060)、和国家留学基金委(202008090261)的共同资助。
这是马军同学本科期间以第一作者发表的第2篇论文(详见录 1),第一篇SCIE学术论文(详见录2)。此篇论文也是王金亮教授导师团队 2023年发表的第10篇 SCI/SCIE 论文,让我们恭喜马军同学!希望他再接再厉!也热烈祝贺团队取好成绩!
附录 1 论文相关信息
标题:A landscape-based ecological hazard evaluation and characterization of influencing factors in Laos
作者:Jun Ma1,2, Vadim Khromykh2, Jinliang Wang1,3,4, *, Jianpeng Zhang1,3,4, Wenjuan Li5, Xuzheng Zhong1,3,4
通讯作者:Jinliang Wang
作者单位:
1 Faculty of Geography, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, China
2Faculty of Geology and Geography, Tomsk State University, Tomsk 634050, Russia
3Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing for Universities in Yunnan, Kunming 650500, China
4Center for Geospatial Information Engineering and Technology of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650500, China
5Faculty of Economics and Management, Tomsk State University, Tomsk 634050, Russia
* Corresponding author:
E-mail: jlwang@ynnu.edu.cn (JW)
出版物: Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution
摘要:The study of the spatiotemporal evolution of landscape ecological hazard and human and natural influences is essential for conservative management and regional sustainable development. This study applied a landscape pattern analysis method and geodetector to multi-source data for 2000, 2010, and 2020 to analyze changes in and drivers of landscape ecological hazard in Laos. The results indicated that: (1) There were more prominent changes in landscape types in Laos. Forest area decreased, whereas the areas of other landscape types increased. There was an overall steady change in the landscape patterns of Laos. Besides for significant changes in the artificial surface landscape index, landscape indices remained stable; (2) The cumulative high and extreme ecological hazard areas increased by 1,947.81 km2, whereas the cumulative areas of low and minimal ecological hazard decreased by 8,461.8 km2. Areas of low and moderate ecological hazard accounted for > 85% of the total area. Areas of low ecological hazard were mainly in the northwest and southeast. The area of high ecological hazard was concentrated in the central and northeastern regions. The distributions of different landscape ecological hazards in Laos during the study period were similar, with general patterns of decreasing hazard from north to south; (3) A positive Moran’s I of landscape ecological hazard in Laos was obtained. While the agglomeration effect was pronounced, it decreased over time, resulting in a weakening in spatial autocorrelation. A significant positive autocorrelation was observed in the spatial distribution of landscape ecological hazard in the study area. Agglomerated areas of high and low ecological hazard were mainly concentrated in the northeast and southeast, respectively; (4) The spatiotemporal evolution of landscape ecological hazard in Laos over the last 20 years could be attributed to interactions between natural and anthropogenic influences. Natural influences were a significant driver of changes to landscape ecological hazard in Laos, with annual precipitation and average temperature being the most significant. Anthropogenic influences, including socioeconomic factors and regional accessibility, significantly impacted local ecological deterioration in Laos.
关键字:landscape ecological hazard; landscape pattern; spatial autocorrelation; Geodetector; risk management; Laos
附录2 马军同学发表论文清单
自 2020 年 9 月攻读博士至今,马军同学在王金亮教授指导下发表了 2 篇SCI论文,信息如下:
[2]Jun Ma, Vadim Khromykh, Jinliang Wang*, Jianpeng Zhang, Wenjuan Li, Xuzheng Zhong. ,A landscape-based ecological hazard evaluation and characterization of influencing factors in Laos[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1276239.
(中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2022年12月二区,2023年最新IF:3.0)
[1]Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Khromykh, V.; Li, J.; Zhong, X. Global Leaf Area Index Research over the Past 75 Years: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis[J]. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043072
(中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2022年12月三区,2023年最新IF:3.9)
附录 3 王金亮教授团队 2023 年发表论文清单
自2023年01月01日至12月1日,王金亮教授导师团队发表学术论文12篇,其中SCIE论文9篇,CSCD4篇,普刊1篇。具体信息如下:
[15]Jun Ma, Vadim Khromykh, Jinliang Wang*, Jianpeng Zhang, Wenjuan Li, Xuzheng Zhong. ,A landscape-based ecological hazard evaluation and characterization of influencing factors in Laos[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1276239.
(中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2022年12月二区,2023年最新IF:3.0)
[14] Ding X, Shao X, Wang J*, Peng S, Shi J. Research on the Spatial-Temporal Pattern Evolution and Driving Force of Ecological Environment Quality in Kunming City Based on Remote Sensing Ecological Environment Index in the Past 25 Years[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies. 2023. doi:10.15244/pjoes/173102.
[13]丁雪,王金亮等.2000—2020年滇中城市群生态环境质量动态监测及空间格局演变[J].水土保持通报,2023,43(03):96-104+128.(CSCD)DOI:10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2023.03.013
[12] Yongcui Lan, Jinliang Wang*, Qianwei Liu, Fang Liu, Lanfang Liu, Jie Li, Mengjia Luo. Identification of critical ecological restoration and early warning regions in the five-lakes basin of central Yunnan[J]. Ecological Indicators,2023.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111337. (中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2021 年 12 月最新基础版二区,升级版二区,2023年最新IF:6.9)
[11] Luo M, Wang J, Li J, Sha J, He S, Liu L, et al. (2023) The response of ecological security to land use change in east and west subtropical China. PLoS ONE 18(11): e0294462. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0294462(2021年12月基础版三区,2022年12月最新升级版三区,2023年最新IF:3.7)
[10]Sikai Wang, Suling He, Jinliang Wang *, Jie Li, Xuzhen Zhong, Janine Cole, Eldar Kurbanov, Jinming Sha. Analysis of Land Use/Cover Changes and Driving Forces in a Typical Subtropical Region of South Africa[J], Remote Sensing. 2023,15(19): 4823. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194823 (2021年12月基础版二区,2022年12月最新升级版二区,2023年最新IF:5.349)
[9] Hong Zhu, Feng Cheng, Jinliang Wang*, Yuanmei Jiao, Jingchun Zhou, Jinming Sha, Fang Liu, and Lanping Nong. Variation in the Ecological Carrying Capacity and Its Driving Factors of the Five Lake Basins in Central Yunnan Plateau, China[J]. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914442(中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版三区,2022年12月最新升级版三区,2023年最新IF3.889)
[8] 邵大江,叶辉,王金亮*,周京春,角媛,沙晋明. 基于机器学习均值化的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 45(3): 653-665. DOI:10.7540/j.ynu.20220109. (CSCD核心库)
[7] Jie Li, Hui Wang, Jinliang Wang*, Jianpeng Zhang, Yongcui Lan, Yuncheng Deng. Combining Multi-Source Data and Feature Optimization for Plastic-Covered Greenhouse Extraction and Mapping Using the Google Earth Engine: A Case in Central Yunnan Province, China [J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15, 3287. DOI: https:// doi.org/10.3390/rs15133287. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版二区,2022年12月最新升级版二区Top,2023年最新IF5.349)
[6]张建鹏;王金亮*;刘广杰;麻卫峰;刘钱威;邓云程. 基于地基雷达点云主方向的林下植被自动滤除[J], 遥感技术与应用, 2023,38(2):405-412. DOI:10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2023.2.0405 (CSCD核心库)
[5]何苏玲,贺增红,潘继亚,王金亮*.基于多模型的县域土地利用/土地覆盖模拟[J/OL].自然资源遥感. 2023-04-03网络首发. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1759.P. 20230331.1810.004.html (CSCD核心库)
[4]成钊,王金亮*,何苏玲,祁兰兰. 基于多源数据的滇中地区生态韧性度研究[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 2023, 35(02):7-16
[3] Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang*, Weifeng Ma, Yuncheng Deng, Jiya Pan, Jie Li. Vegetation Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data of Urban Plots Based on Point Cloud Neighborhood Features [J]. Forests, 2023, 14(4), 691. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040691. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版三区, 2022年12月最新升级版二区,2022年IF 3.282)
[2] Jun Ma, Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang *, Vadim Khromykh, Jie Li, Xuzheng Zhong. Global Leaf Area Index Research over the Past 75 Years: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis [J]. Sustainability, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043072. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版三区,2022年12月最新升级版三区,2022年IF 3.889)
[1] Lei Liang, Jinliang Wang*, Fei Deng, Deyang Kong. Mapping Pu'er tea plantations from GF-1 images using Object-Oriented Image Analysis (OOIA) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) [J]. PLOS ONE, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone. 0263969. (中科院SCI期刊分区: 2021年12月基础版三区,2022年12月最新升级版三区,2022年IF 3.752)
(云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室 供稿)
地址:云南省昆明市呈贡区云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院413
邮箱:ynnurs@163.com 电话:0871-65941202 技术支持:蓝队云
版权所有:Copyright © 2016-2018 云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室. All Rights Reserved