王金亮教授团队学术论文在SCIE二区期刊Ecological Indicators上线发表
2023年12月31日,以叶辉(云南师范大学地理学部地图学与地理信息系统专业2019级硕士)为第一作者,王金亮教授为通讯作者所撰写的题为“Landscape ecological risk assessment study of the Yunnan section of the Tropic of Cancer”的学术论文在SCI/SCIE二区期刊《Ecological Indicators》上线发表(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111517).

自然景观是生态系统的重要组成部分,其稳定性和多样性对维持区域生态系统功能至关重要。科学合理的区域景观生态风险评价是开展生态系统安全评价、优化生态系统功能分区、构建景观安全格局等活动的基础。以北回归线云南段为研究对象,利用Landsat 8遥感数据对景观类型进行分类,构建生态风险指数。利用ArcGIS、GEE、Fragstats4.2等软件平台,对北回归线云南段生态风险进行了评价和空间特征分析,结果表明:①北回归线云南段生态风险总体水平较低;低生态风险区面积为19100.35 km2,占研究总面积的34.09%;高生态风险区面积为2032.91 km2,仅占研究总面积的3.63%。②低生态风险区和低生态风险区景观类型以林地景观为主,分别占90.93%和62.19%;相反,高生态风险区和高生态风险区以耕地为主,分别占67.75%和95.61%。这凸显了加强林业发展和控制耕地扩张对缓解区域景观生态风险的重要性。③景观生态风险较高的区域主要集中在砚山县西北部、耿马县南部和文山市北部。这些地区容易受到集约化耕作、极端天气和喀斯特地质环境的影响。墨江县中东部、砚山县西部、文山市北部是生态风险较高的区域。这些地区主要受到城市经济发展、大量建设项目导致森林砍伐和草地退化以及人口大量增加对耕地的大量需求的影响。④北回归线云南段生态风险空间格局为正,Moran’s I指数大于0.6。Z评分显著高于参考值2.58, p < 0.01。这表明空间分布特征具有很强的空间自相关和高度的正相关。
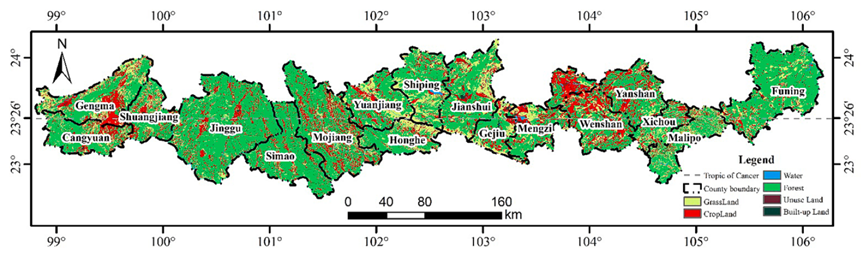
Fig. 1. Supervised Classification Map of GEE Land Use.
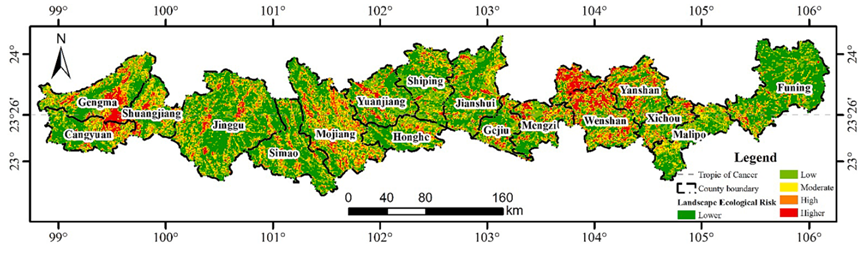
Fig. 2. Spatial Distribution Map of Landscape Ecological Risk Levels in the Yunnan Section of the Tropic of Cancer.
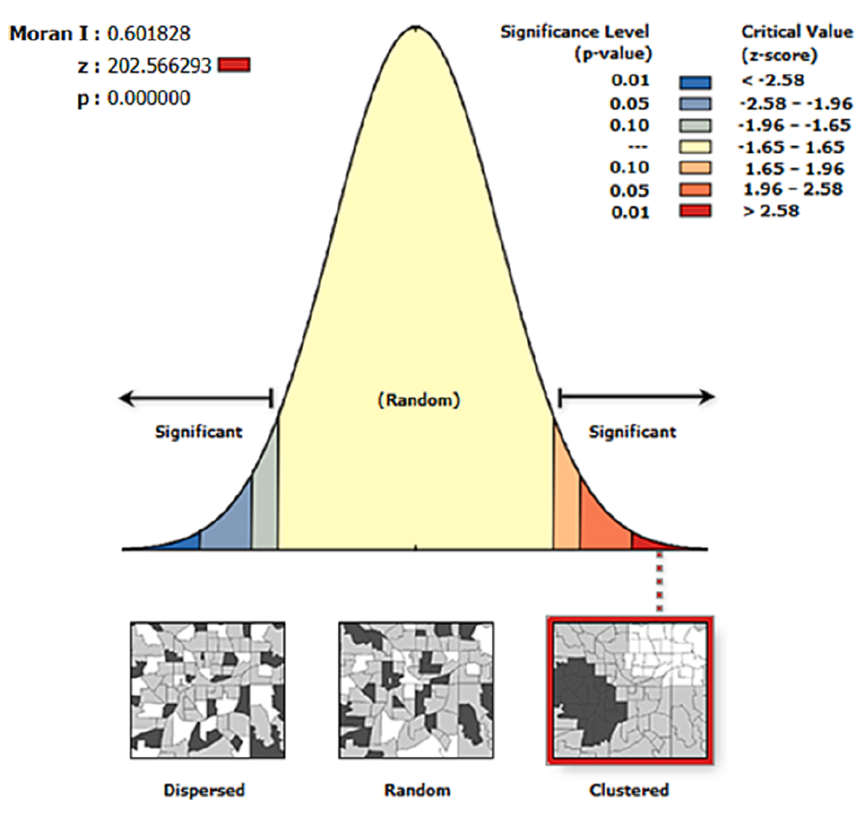
Fig. 3. Spatial autocorrelation characteristics of landscape ecological risk in the Yunnan Section of the Tropic of Cancer
该论文得到了王金亮教授主持的云南省基础研究基金重点项目“北回归线(云南段)旅游大健康产业地理环境考察”( 2019FA017),国家重点研发计划政府间/港澳台重点专项项目“利用地理空间技术监测和评估土地利用/土地覆被变化对区域生态安全的影响” (立项编号:2018YFE0184300),欧盟文化执行署(EACEA)伊拉斯谟+国际高等教育能力建设项目 “遥感教育与学习创新(批准号:586037-EPP-1-2017-1-HU-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP)、云南省哲学社会科学重点项目(批准号:ZDZZD201506)的共同资助。
这是叶辉同学硕士期间以第一作者发表的第4篇论文(详见录 1),第一篇SCIE学术论文(详见录2)。此篇论文也是王金亮教授导师团队 2023年发表的第11篇 SCI/SCIE 论文,让我们恭喜叶辉同学!希望他再接再厉!也热烈祝贺团队取好成绩!
附录 1 论文相关信息
标题:Landscape ecological risk assessment study of the Yunnan section of the
Tropic of Cancer
作者:Ye Hui a,b, Bai Die c, Wang Jinliang a,*, Tan Shucheng c, Liu Shiyin b, Wu Xiaoping d
通讯作者:Jinliang Wang
作者单位:
a Department of Geography, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, Yunnan 650500, China
b Institute of International Rivers and Ecological Security, Yunnan University, Kunming, Yunnan 650500, China
c School of Earth Sciences, Yunnan University, Kunming, Yunnan 650500, China
d Pan-Asian Business School, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, Yunnan 650500, China
* Corresponding author:
E-mail: jlwang@ynnu.edu.cn (JW)
出版物:Ecological Indicators
摘要:
Natural landscapes constitute a vital component of ecosystems, and their stability and diversity are essential in maintaining regional ecosystem functions. The scientific and rational assessment of ecological risks in regional landscapes is crucial for activities such as ecosystem security evaluation, optimization of ecosystem function zoning, and establishment of landscape security patterns. We focused on the Yunnan section of the Tropic of Cancer, employing Landsat 8 remote sensing data to categorize landscape types and construct ecological risk indices. Using software platforms such as ArcGIS, GEE, and Fragstats4.2, an evaluation and spatial characteristics analysis of the ecological risk in the Yunnan section of the Tropic of Cancer was conducted, yielding the following findings: ① The overall level of ecological risk within the Yunnan section of the Tropic of Cancer is relatively low. The lower ecological risk zone covers an area of 19,100.35 km2, accounting for 34.09% of the total study area, while the higher ecological risk zone spans 2,032.91 km2, constituting only 3.63% of the total study area. ② Landscape types in areas of lower and low ecological risk are predominantly characterized by woodland landscapes, comprising 90.93% and 62.19%, respectively. Conversely, areas with high ecological risk and higher ecological risk are dominated by cultivated land, representing 67.75% and 95.61%, respectively. This underscores the importance of strengthening forestry development and controlling the expansion of cultivated land to mitigate regional landscape ecological risks. ③Regions with higher ecological risks in the landscape are primarily in the northwestern part of Yanshan County, the southern part of Gengma County, and the northern part of Wenshan city. These areas are susceptible to the impacts of intense farming, extreme weather, and the karst geological environment. In contrast, regions with high ecological risks are in the central and eastern parts of Mojiang County, the western part of Yanshan County, and the northern part of Wenshan city. These areas are mostly influenced by urban economic development, extensive construction projects leading to deforestation and grassland degradation, and the substantial demand for arable land due to a significant population increase. ④ The spatial pattern of ecological risk in the Yunnan section of the Tropic of Cancer, as indicated by Moran's I index, is positive and exceeds 0.6. The Z score significantly surpasses the reference value of 2.58, with p < 0.01. This indicates a strong degree of spatial autocorrelation and a high positive correlation in the spatial distribution characteristics.
关键字:Landscape ecological risk; landscape pattern; landscape disturbance level; landscape loss level; Yunnan section of the Tropic of Cancer
附录2 叶辉同学发表论文清单
自 2019 年 9 月攻读硕士至今,叶辉同学在王金亮教授指导下发表了 4 篇论文,其中1篇SCI论文,信息如下:
[1]叶辉,王金亮*,赵娟娟.基于多源数据的北回归线(云南段)地质旅游资源调查与开发潜力评价[J].云南大学学报(自然科学版),2020,42(06):1110-1120.(CSCD 核心库)
[2]叶辉,王金亮*,赵娟娟.基于DPSIR-EES模型的北回归线(云南段)生态安全评价[J].水土保持研究,2021,28(03):291-298.(CSCD 扩展库)
[3] YE Hui, BAI Die, WANG Jinliang*, et al. Evaluating the Ecological Security of Land Resources based on Multi-source Data in the Altay Region of China [J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology,2021,12(06):757-765.(CSCD 核心库)
[4] Ye Hui, Bai Die, Wang Jinliang*, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment study of the Yunnan section of the Tropic of Cancer [J]. Ecological Indicators, 158 (2023) 111517. (中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2023年12月二区 Top,2023年最新IF:6.9)
附录 3 王金亮教授团队 2023 年发表论文清单
自2023年01月01日至12月31日,王金亮教授导师团队发表学术论文17篇(仅仅统计王金亮教授为通讯作者的论文),其中SCIE论文11篇,CSCD论文5篇,普刊论文1篇。具体信息如下:
[17] Ye Hui, Bai Die, Wang Jinliang*, et al. Landscape ecological risk assessment study of the Yunnan section of the Tropic of Cancer [J]. Ecological Indicators, 158 (2023) 111517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111517
(中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2023年12月二区 Top,2023年最新IF:6.9)
[16]Jun Ma, Vadim Khromykh, Jinliang Wang*, Jianpeng Zhang, Wenjuan Li, Xuzheng Zhong. ,A landscape-based ecological hazard evaluation and characterization of influencing factors in Laos[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1276239.
(中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2022年12月二区,2023年最新IF:3.0)
[15] Ding X, Shao X, Wang J*, Peng S, Shi J. Research on the Spatial-Temporal Pattern Evolution and Driving Force of Ecological Environment Quality in Kunming City Based on Remote Sensing Ecological Environment Index in the Past 25 Years[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies. 2023. doi:10.15244/pjoes/173102.
(中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2022年12月四区,2023年最新IF:1.80)
[14]丁雪 ,冯婧文,黄园园,施骏骋,王金亮*.2000—2020年滇中城市群生态环境质量动态监测及空间格局演变[J].水土保持通报,2023,43(03):96-104+128.(CSCD)DOI:10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2023.03.013
[13] Yongcui Lan, Jinliang Wang*, Qianwei Liu, Fang Liu, Lanfang Liu, Jie Li, Mengjia Luo. Identification of critical ecological restoration and early warning regions in the five-lakes basin of central Yunnan[J]. Ecological Indicators,2023.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111337. (中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2021 年 12 月最新基础版二区,升级版二区,2023年最新IF:6.9)
[12] Luo M, Wang J*, Li J, Sha J, He S, Liu L, et al. (2023) The response of ecological security to land use change in east and west subtropical China. PLoS ONE 18(11): e0294462. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0294462(2021年12月基础版三区,2022年12月最新升级版三区,2023年最新IF:3.7)
[11]钟旭珍,王金亮*,邓云程,李杰,吴瑞娟,董品亮.怒江 ̄萨尔温江流域植被覆盖时空变化趋势及驱动力研究[J].生态学报, 2023,43(24). DOI: 10.20103/j.stxb.202305311156.网络首发地址:https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2031.Q.20231109.1009.004 (CSCD核心库)
[10]Sikai Wang, Suling He, Jinliang Wang *, Jie Li, Xuzhen Zhong, Janine Cole, Eldar Kurbanov, Jinming Sha. Analysis of Land Use/Cover Changes and Driving Forces in a Typical Subtropical Region of South Africa[J], Remote Sensing. 2023,15(19): 4823. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194823 (2021年12月基础版二区,2022年12月最新升级版二区,2023年最新IF:5.349)
[9] Hong Zhu, Feng Cheng, Jinliang Wang*, Yuanmei Jiao, Jingchun Zhou, Jinming Sha, Fang Liu, and Lanping Nong. Variation in the Ecological Carrying Capacity and Its Driving Factors of the Five Lake Basins in Central Yunnan Plateau, China[J]. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914442(中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版三区,2022年12月最新升级版三区,2023年最新IF3.889)
[8] 邵大江,叶辉,王金亮*,周京春,角媛,沙晋明. 基于机器学习均值化的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 45(3): 653-665. DOI:10.7540/j.ynu.20220109. (CSCD核心库)
[7] Jie Li, Hui Wang, Jinliang Wang*, Jianpeng Zhang, Yongcui Lan, Yuncheng Deng. Combining Multi-Source Data and Feature Optimization for Plastic-Covered Greenhouse Extraction and Mapping Using the Google Earth Engine: A Case in Central Yunnan Province, China [J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15, 3287. DOI: https:// doi.org/10.3390/rs15133287. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版二区,2022年12月最新升级版二区Top,2023年最新IF5.349)
[6]张建鹏;王金亮*;刘广杰;麻卫峰;刘钱威;邓云程. 基于地基雷达点云主方向的林下植被自动滤除[J], 遥感技术与应用, 2023,38(2):405-412. DOI:10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2023.2.0405 (CSCD核心库)
[5]何苏玲,贺增红,潘继亚,王金亮*.基于多模型的县域土地利用/土地覆盖模拟[J/OL].自然资源遥感. 2023-04-03网络首发. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1759.P. 20230331.1810.004.html (CSCD核心库)
[4]成钊,王金亮*,何苏玲,祁兰兰. 基于多源数据的滇中地区生态韧性度研究[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 2023, 35(02):7-16
[3] Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang*, Weifeng Ma, Yuncheng Deng, Jiya Pan, Jie Li. Vegetation Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning Data of Urban Plots Based on Point Cloud Neighborhood Features [J]. Forests, 2023, 14(4), 691. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040691. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版三区, 2022年12月最新升级版二区,2022年IF 3.282)
[2] Jun Ma, Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang *, Vadim Khromykh, Jie Li, Xuzheng Zhong. <span style="font-size: 16px;line-h
地址:云南省昆明市呈贡区云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院413
邮箱:ynnurs@163.com 电话:0871-65941202 技术支持:蓝队云
版权所有:Copyright © 2016-2018 云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室. All Rights Reserved