资源与环境遥感团队学术论文在SCI二区期刊《Forests》上线发表
2024年04月05日,以徐海潮(云南师范大学地理学部地图学与地理信息系统专业2023级硕士研究生)为第一作者,王金亮教授为通讯作者所撰写的题为“Temporal–Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Forest Fires in the Tropic of Cancer (Yunnan Section)”的学术论文在SCI二区期刊《Forests》上线发表(https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040661).

森林火灾往往造成了大量人员伤亡与财产损失,探究区域森林火灾发生的时空规律以及影响因素具有重要现实意义。研究以北回归线(云南段)穿过的州(市)作为研究区,基于火烧迹地数据,结合气候、地形、植被等自然因素和离居民点距离、人口密度等人为活动因素,采用二项分类logistic回归与增强回归树等方法,对研究区2000-2020年的森林火灾时空格局及驱动因子进行了分析。结果表明:(1)2000-2020年期间,研究区森林火灾面积整体呈现波动式下降的趋势,2010年是森林火灾高发期,2010年后研究区森林火灾面积大幅减少。(2)研究区森林火灾总体呈现东多西少的空间格局,东部的文山州与红河州的森林火灾面积较大,占68%,而西部普洱市、临沧市、玉溪市面积较小,仅占32%。(3)降水、气温因子在两个驱动力分析模型中贡献率排名都位于前2名,说明降水、气温对研究区森林火灾的发生有显著影响。
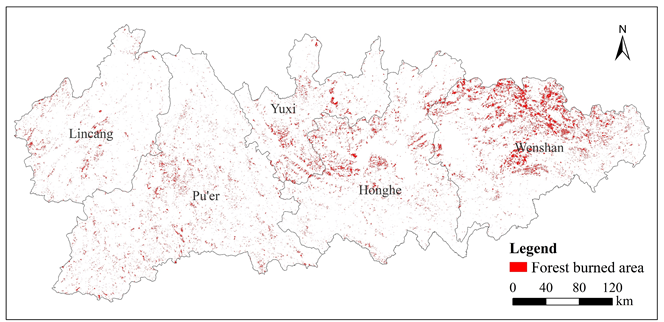
Fig. 1. Distribution map of forest burned area in prefectures (cities) of the Tropic of Cancer (Yunnan section) from 2000 to 2020
该论文得到了王金亮教授主持的云南省西南联合研究生院科技专项-基础研究和应用基础研究重大项目(202302AO370003)、云南省基础研究项目(2019FA017)、国家自然基金项目(41961060 )与云南师范大学研究生科研创新基金(YJSJJ23-B141)的共同资助。
这是徐海潮同学硕士期间以第一作者发表的第1篇SCI学术论文(详见附录1),此篇论文也是王金亮教授导师团队2024年发表的第3篇SCI/SCIE论文,让我们恭喜徐海潮同学!希望她再接再厉!也热烈祝贺团队取好成绩!
附录 1 论文相关信息
标题: Temporal–Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Forest Fires in the Tropic of Cancer (Yunnan Section)
作者:Haichao Xu 1,2,3, Rongqing Han 2, Jinliang Wang 1,3,4,5,* and Yongcui Lan 1,3,4,5
通讯作者:Jinliang Wang
作者单位:
1 Faculty of Geography, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, China
2 College of Geography and Environment, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
3 Southwest United Graduate School, Kunming 650092, China
4 Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing for Universities in Yunnan, Kunming 650500, China
5 Center for Geospatial Information Engineering and Technology of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650500, China
Corresponding author:
E-mail: jlwang@ynnu.edu.cn
出版物:Forests
摘要:
Forest fires often cause many casualties and property losses, and it is important to explore the time and space laws of forest fires and the influencing factors. The present study used the cities (prefectures) crossed by the Tropic of Cancer (Yunnan section) as the study area. Based on burned land data, a combination of natural factors, such as climate, topography, vegetation, and human activities, such as distance from settlements and population density, a binary logistic regression model, and a boosted regression tree model, were used to analyze the temporal–spatial characteristics and influencing factors of forest fires in 2000 to 2020. The following results were obtained: (1) During 2000–2020, the overall forest fire area in the study area showed a trend of fluctuating decline. The high incidence period of forest fires occurred in 2010. After 2010, the forest fire area in the study area was greatly reduced. (2) The forest fire area in the study area was greater in the east and less in the west. The forest fire areas in Wenshan Prefecture and Honghe Prefecture in the east were larger, accounting for 68%, and the forest fire areas in Pu’er City, Lincang City, and Yuxi City in the west were smaller, accounting for only 32%. (3) The contribution rate of the average precipitation and average temperature factors ranked in the top two in the two driving force analysis models, which indicated that precipitation and temperature had a significant effect on the incidence of forest fires in the study area.
关键字:forest fire; temporal and spatial distribution; binary logistic regression (BLR); boosted regression tree (BRT); fire occurrence factors; Tropic of Cancer (Yunnan section)
附录 2 王金亮教授团队 2024 年发表论文清单
自2024年01月01日至04月05日,王金亮教授导师团队发表学术论文3篇(仅仅统计王金亮教授为通讯作者的论文),其中SCI/SCIE论文3篇。具体信息如下:
[3] Xu, Haichao, Rongqing Han, Jinliang Wang*, and Yongcui Lan.Temporal–Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Forest Fires in the Tropic of Cancer (Yunnan Section)[J]. Forests, 2024, 15, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040661
[2] Yanke Zhang, Tengfei Gu, Suling He, Feng Cheng, Jinliang Wang*, et al. Extreme drought along the tropic of cancer (Yunnan section) and its impact on vegetation[J]. Scientific reports, 2024, 14, 7508. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-58068-w.
[1]Di Duan, Yuncheng Deng, Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang*, et al. Influence of VF and SOR-Filtering Methods on Tree Height Inversion Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle LiDAR Data[J]. Drones, 2024, 8(4), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8040119.
(云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室 供稿)
地址:云南省昆明市呈贡区云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院413
邮箱:ynnurs@163.com 电话:0871-65941202 技术支持:蓝队云
版权所有:Copyright © 2016-2018 云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室. All Rights Reserved