王金亮导师团队学术论文在 SCIE 期刊Remote Sensing上线发表
2022 年 11 月 17 日,以邓云程(云南师范大学地理学部地图学与地理信息系统专业 2020 级硕士研究生)为第一作者,王金亮教授为通讯作者所撰写的题为“Mapping of Forest Biomass in Shangri-La City Based on LiDAR Technology and Other Remote Sensing Data”的学术论文在SCIE期刊 《Remote Sensing》 (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月最新基础版二区,升级版二区,2022年IF 5.349)上线发表 (https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225816)。
森林生态系统是一个巨大的碳汇,快速准确的估算森林地上生物量是更好研究碳平衡的重要前提。然而当前的生物量制图成果多依赖于大量的实测数据,且区域性的估算结果空间分辨率不高。为进一步提高估算效率,获取高空间分辨率森林生物量估算结果,研究以星载激光雷达数据和光学遥感影像为主要基础数据,探求一种适合高山峡谷地区区域尺度生物量快速估算的方法。研究利用ICESat-2星载激光雷达数据、光学遥感数据Landsat8 OLI、Sentinel-2和微波遥感数据Sentinel-1构建香格里拉市高山峡谷地区森林冠层高度外推模型,获取香格里拉市30m分辨率连续冠层高度;结合实测数据构建香格里拉市林木树高-胸径生长模型,实现连续胸径的估算;最终,构建基于森林平均胸径的森林地上生物量/碳储量估算模型,完成香格里拉市30m空间分辨率森林地上生物量/碳储量制图。研究结果显示,香格里拉市森林冠层高度主要集中在2.82m-30.96m范围内,利用机载LiDAR生成的CHM进行精度验证,R2=0.7143;冠层高度反演模型中地理空间位置因子(Longitude、Latitude)、地形因子(slope、elevation)、植被指数(NBR、NDGI、NDVI)等因子对反演结果的影响最大;通过树高胸径关系估算的香格里拉市林木胸径主要集中在20cm-30cm范围内,通过与实测数据进行验证R2均大于0.7;最后,研究建立的香格里拉市森林地上生物量估算模型估算得到2020年研究区森林地上生物量为1.28 × 108 t,碳储量为6.41 × 107 t,估算精度达到了92.28%。
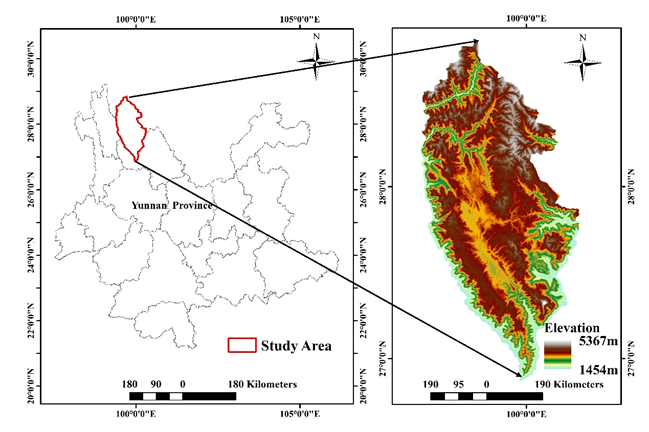
Figure 1. Location of the Shangri-La study area in China.
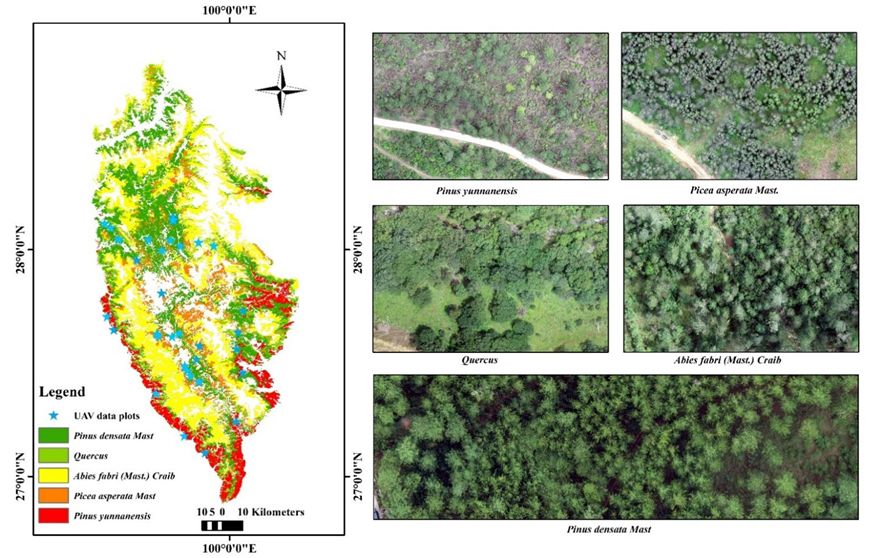
Figure 2. The location of UAV survey plots and the orthophoto of four tree species.
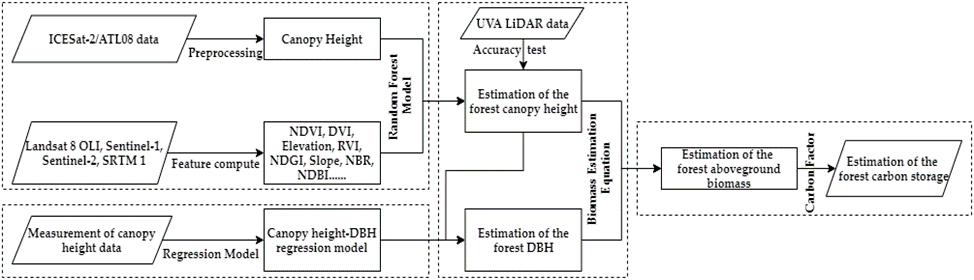
Figure 3. Flow chart of the proposed methodology for canopy height estimation and forest biomass mapping.
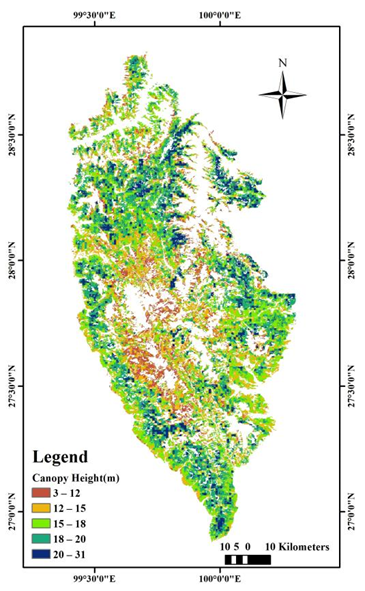
Figure 4. Forest canopy height mapping in Shangri-La City
该论文得到了王金亮教授主持的国家自然科学基金 (41961060)和麻卫峰老师主持的云南省教育厅科学研究基金(2021J0438)资助。
这是邓云程同学读硕士研究生以来发表的首篇 SCI/SCIE 学术论文,是他的硕士期间发表的第二篇学术论文(详见录 1、2),也是王金亮教授导师团队 2022年的发表第13篇 SCI/SCIE 论文(详见录 3),让我们恭喜邓云程同学!希望他再接再厉!也热烈祝贺团队取好成绩!
附录 1 论文相关信息
标题:Mapping of Forest Biomass in Shangri-La City Based on LiDAR Technology and Other Remote Sensing Data
作者:Yuncheng Deng1,2,3 , Jiya Pan1,2,3 , Jinliang Wang1,2,3 , Qianwei Liu1,2,3, Jianpeng Zhang1,2,3
通讯作者:Jinliang Wang
作者单位:
1 Faculty of Geography, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, Yunnan, China;
2 Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing for Universities in Yunnan, Kunming, Yunnan 650500, China;
3 Center for Geospatial Information Engineering and Technology of Yunnan Province, Kunming, Yunnan, China;
出版物: Remote Sensing
摘要: Forest ecosystems can be regarded as huge carbon sinks. In order to effectively assess carbon balance in such ecosystems, rapid and accurate estimation of the aboveground biomass of a forest is critically needed. However, the current methods for biomass estimation and mapping are of limited spatial resolution and mostly depend on large numbers of measurements. In order to obtain better biomass estimation outcomes with higher spatial resolution, a rapid method is introduced for region-scale biomass estimation in alpine and canyon areas using space-borne light detection and ranging (LiDAR) data and optical remote-sensing images. Specifically, we explored alpine and canyon areas in Shangri-La City in China using space-borne LiDAR data from ICESAT-2 and optical remote-sensing images from Landsat8 OLI, Sentinel-2, and Microwave remote sensing Sentinel-1. An extrapolation model of the forest canopy heights in these areas was constructed with a 30-m resolution of continuous canopy height outputs. For continuously estimating the diameter at breast height (DBH) in Shangri-La City, a tree height-DBH growth model was constructed based on the LiDAR and remote-sensing measurements. Finally, based on the average DBH of the explored forests, a model was constructed for estimating and mapping the aboveground biomass and carbon storage in Shangri-La with a spatial resolution of 30 m. The results show that the forest canopy height in Shangri-La City is mainly in the range of 2.82 m–30.96 m, and that the estimation accuracy is verified by the LiDAR-based canopy height model (CHM) with a coefficient of determination of R2 = 0.7143. The inversion results were still largely affected by geospatial location factors (longitude, latitude), terrain factors (slope, elevation), and vegetation indices (NBR, NDGI, NDVI). Based on the relationship between the tree height and the DBH, the DBH of trees in Shangri-La City was estimated to be mainly in the range of 20 cm to 30 cm, and this estimate was verified by actual measurements with R2 greater than 0.7 all. Finally, the established model estimated the aboveground forest biomass and carbon storage of the study area of Shangri-La City in 2020 to be 1.28 × 108 t and 6.41 × 107 t, respectively. These estimates correspond to total accuracies of 92.28%, respectively.
关键字:LiDAR; canopy height; DBH; forest aboveground biomass; forest carbon storage
附录2 邓云程同学发表SCI论文清单
自2020年9月攻读硕士至今,邓云程同学在王金亮教授指导下发表了2篇学术论文,其中1篇CSCD学术论文,1篇SCI学术论文,信息如下:
[1]邓云程,王金亮*,刘钱威,冯宝坤,张建鹏.提取林木胸径的F-LS算法[J].遥感信息,2022, 37(5): 77-84. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2022.05.012 (CSCD核心库)
[2]Yuncheng Deng, Jiya Pan, Jinliang Wang*, Qianwei Liu, Jianpeng Zhang. Mapping of Forest Biomass in Shangri-La City Based on LiDAR Technology and Other Remote Sensing Data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022,14,5816. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225816. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月最新基础版二区,升级版二区,2022年IF 5.349)
附录 3 王金亮团队 2022 年 1 月至目前发表论文清单
自2022年1月至11月17日,王金亮教授团队发表学术论文17篇,其中13篇SCI/SCIE 论文、4篇CSCD论文,具体信息如下:
[17]Yuncheng Deng, Jiya Pan, Jinliang Wang*, Qianwei Liu, Jianpeng Zhang. Mapping of Forest Biomass in Shangri-La City Based on LiDAR Technology and Other Remote Sensing Data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022,14,5816. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225816. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月最新基础版二区,升级版二区,2022年IF 5.349)
[16]邓云程,王金亮*,刘钱威,冯宝坤,张建鹏.提取林木胸径的F-LS算法[J].遥感信息,2022, 37(5): 77-84. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2022.05.012 (CSCD核心库)
[15] Yongcui Lan, Jinliang Wang*, Wenying Hu, Eldar Kurbanov, Janine Cole, Jinming Sha, Yuanmei Jiao, Jingchun Zhou. Spatial pattern prediction of forest wildfire susceptibility in Central Yunnan Province, China based on multivariate data[J]. Natural Hazards, 2022, Online. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05689-x. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月最新基础版三区,升级版三区,2021年IF 3.158)
[14] Jiya Pan , Cheng Wang, Jinliang Wang* , Fan Gao, Qianwei Liu , Jianpeng Zhang, and Yuncheng Deng. Land Cover Classification Using ICESat-2 Photon Counting Data and Landsat 8 OLI Data: A Case Study in Yunnan Province, China[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2022.3209725. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版三区,升级版二区,2021年IF 5.343)
[13] Suling He, Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, and Fang Liu. Evaluation and analysis of upscaling of different Land Use /Land Cover products (FORM-GLC30, GLC_FCS30, CCI_LC, MCD12Q1 and CNLUCC): a case study in China[J]. Geocarto International, 2022. DOI: 10.1080/10106049.2022.2127926. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版二区,升级 版,2021年IF 4.889)
[12]Juncheng Shi, Cheng Wang, Jinliang Wang*, Xiaohuan Xi*, Xuebo Yang, and Xue Ding*. Study on the LAI and FPAR inversion of maize from airborne LiDAR and hyperspectral data[J] INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF REMOTE SENSING 2022, VOL. 43, NO. 13, 4793-4809 HTTPS://DOI.ORG/10.1080/01431161.2022.2121187. (中科院SCI期刊分区: 2021年12月最新基础版三区,升级版三区;2021年IF 3.531)
[11] Chen Y, Wang J*, Kurbanov E, Thomas A, Sha J, Jiao Y, et al. Ecological security assessment at different spatial scales in central Yunnan Province, China[J]. PLoS ONE, 2022, 17(6): e0270267. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0270267. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版三区,升级版三区;2022年最新IF 3.752)
[10] Jiya Pan, Jinliang Wang*, Fan Gao, and Guangjie Liu. Quantitative estimation and influencing factors of ecosystem soil conservation in Shangri-La, China[J]. Geocarto International, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2091160. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版二区,升级版三区;2021年IF 4.889)
[9] Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang*, Feng Cheng, Weifeng Ma, Qianwei Liu, Guangjie Liu. Natural forest ALS-TLS point cloud data registration without control points[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2022, Online. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-022-01499-w. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021 年12月基础版SCIE二区,升级版SCIE二区;2021年IF 2.149)
[8] PAN, J. Y. ,WANG, J. L.* , LIU, G. J. ,GAO, F. Estimation of ecological asset values in Shangri_la based on remotely sensed data [J]. Applied ecology and environmental research, 2022, 20(4):2879-2895. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15666/aeer/2004_28792895 . (中科院SCI 期刊分区:2021年12月基础版SCIE四区,升级版SCIE四区;2020-2021最新IF: 0.711)
[7]Jie Li, Suling He, Jinliang Wang*, Weifeng Ma, Hui Ye. Investigating the spatiotemporal changes and driving factors of nighttime light patterns in RCEP Countries based on remote sensed satellite images [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 131944. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.jclepro.2022.131944. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版SCIE一区,升级版 SCIE一区;Top:是;2020-2021最新IF: 9.297)
[6]何苏玲,王金亮*,角媛梅,周京春,农兰萍,朱泓.国土空间规划视角下资源环境承载力评价分析——以昆明市为例[J], 中国农业资源与区划, 2021,43(4): 119-127. DOI: 10.7621 /CJARRP. 1005-9121. 20220413 (CSCD核心库; CSSCI)
[5]潘继亚, 王金亮, 高帆. 滇西北高山峡谷典型区土地利用变化与生态安全评价 研究 [J]. 生态科学, 2022, 41(2): 29–40. (CSCD扩展库,北大核心)
[4] Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, Jun Zhang, Chenli Liu, Suling He, Lanfang Liu. Growing-season vegetation coverage patterns and driving factors in the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor based on Google Earth Engine and geographic detector [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 136, 108620. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108620. (中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2021年12 月基础版 SCIE二区,升级版SCIE二区;2022最新IF: 6.263)
[3]农兰萍,王金亮*,玉院和.基于地理加权回归模型和不同植被特征参数的 TRMM 3B43 降尺度研究——以云南省为例[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(01): 99-110+117. DOI:10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2022.01.011. ( CSCD 核心库)
[2] Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang*, Pinliang Dong, Weifeng Ma, Yicheng Liu, Qianwei Liu, Zhiyan Zhang. Tree stem extraction from TLS point-cloud data of natural forests based on geometric features and DBSCAN[J]. Geocarto International, Published online: 08 Feb 2022. DOI: 10.1080/10106049.2022.2034988 (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版SCIE区,升级版SCIE三区;2021年IF 4.889)
[1] Yuanhe Yu, Xingqi Sun, Jinliang Wang*, Jianpeng Zhang. Using InVEST to evaluate water yield services in Shangri-La, Northwestern Yunnan, China[J]. Peer J, 2022, online. DOI: doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12804 (中科院 SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版SCIE三区,升级版SCIE三区;2020-2021年IF: 2.984)
(云南高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室 供稿)
地址:云南省昆明市呈贡区云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院413
邮箱:ynnurs@163.com 电话:0871-65941202 技术支持:蓝队云
版权所有:Copyright © 2016-2018 云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室. All Rights Reserved