王金亮教授团队学术论文在 SCIE 期刊Natural Hazards上线发表
2022 年 10 月 27 日,以兰永翠(云南师范大学地理学部地图学与地理信息系统专业 2021 级硕士研究生)为第一作者,王金亮教授为通讯作者所撰写的题为“Spatial pattern prediction of forest wildfire susceptibility in Central Yunnan Province, China based on multivariate data”的学术论文在 SCI/SCIE期刊 Natural Hazards (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月最新基础版三区,升级版三区,2021年IF 3.158)上线发表 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05689-x.)。
野火是森林生态系统中的重要干扰因素。评估森林野火发生的可能性有助于森林野火的预防、控制和监督。logistic回归模型被广泛用于野火驱动因素的分析以及森林野火易感性的空间分布预测。本研究使用logistic回归方法建立了森林野火易感性的空间预测模型,以2001-2020年的林火数据集为因变量,选取气象、植被、地形、人文以及位置相关的因素作为预测变量,开展了滇中地区森林野火的风险评估。结果表明:(1)温度、植被覆盖率、距水体距离、距道路距离、降水量与森林野火的发生呈正相关。海拔、相对湿度、全球植被湿度指数、风速、坡度、纬度和距居民区的距离与森林野火的发生呈负相关。(2) 森林野火易感性的空间预测模型的拟合效果较好,模型模拟的总体概率为81.6%。滇中地区的森林野火发生的最佳阈值为0.414。当选取的模型变量的显著性水平均小于0.05的情况下,ROC曲线下的面积(AUC)在0.882-0.890之间。(3)玉溪市西南部和曲靖市南部在森林野火高风险地区中所占比例很高,因此,森林野火防治工作应集中在玉溪市和曲靖市中南部。森林野火预防工作应根据当地情况,并遵循合理的应急资源计划和分配。(4)野火驱动因素在不同的时空尺度上对森林野火的发生表现出不同程度的影响。这进一步验证了森林野火诱发和蔓延的潜在机制的复杂性。因此,在森林野火风险评估中,应根据区域特征选择相关的驱动因素。
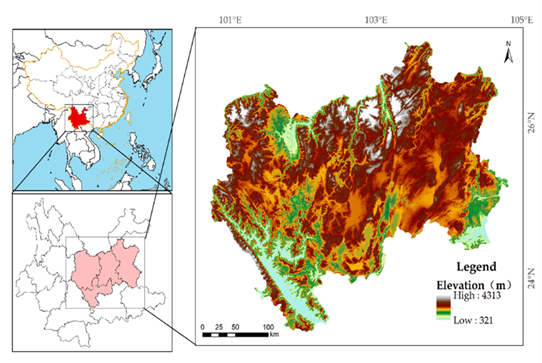
Fig. 1 Map of Central Yunnan Province, China showing the spatial distribution of elevation. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
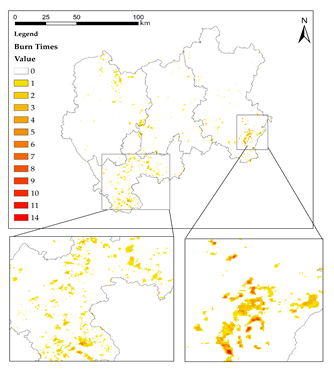
Fig. 2 Maps of Central Yunnan Province (CYP) showing (a) the distribution of burn scars and a statistical summary of repeated burn times in the same area from 2001 to 2020 and (b) distribution of random points
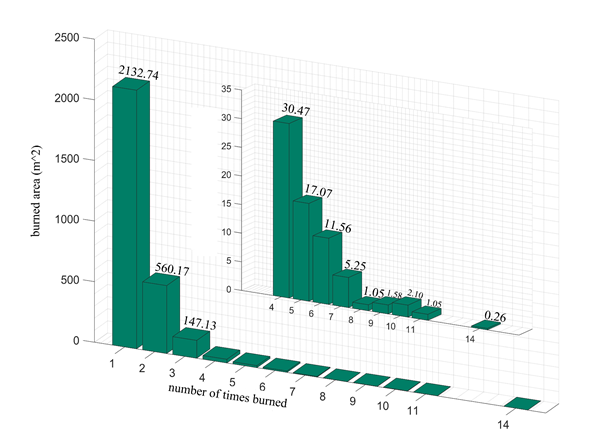
Fig. 3 Statistics of number of times burned in the same burning area in CYP from 2001 to 2020
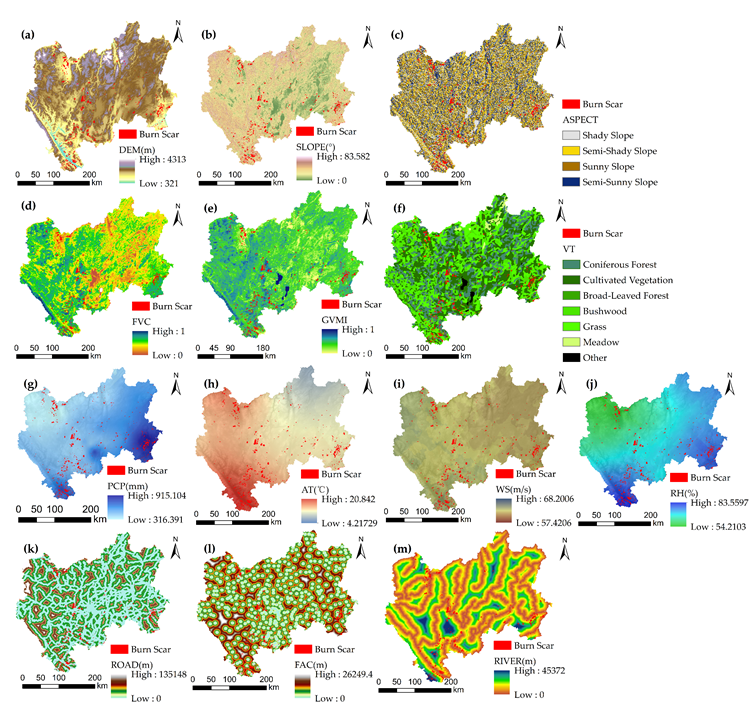
Fig. 4 Spatial distribution of vegetation factors in Central Yunnan Province (CYP), China, (a)Elevation, (b)Slope, (c)Aspect, (d)Fractional Vegetation Cover, (e) Global Vegetation Moisture Index, (f) Vegetation Type, (g) Annual average precipitation for 2001 to 2020, (h) Annual average temperature for 2001 to 2020, (i) Annual average wind speed for 2001 to 2020, (j) Annual average relative humidity for 2001 to 2020, (k) Distance to Road, (l) Distance to Facility, (m) Distance to River.
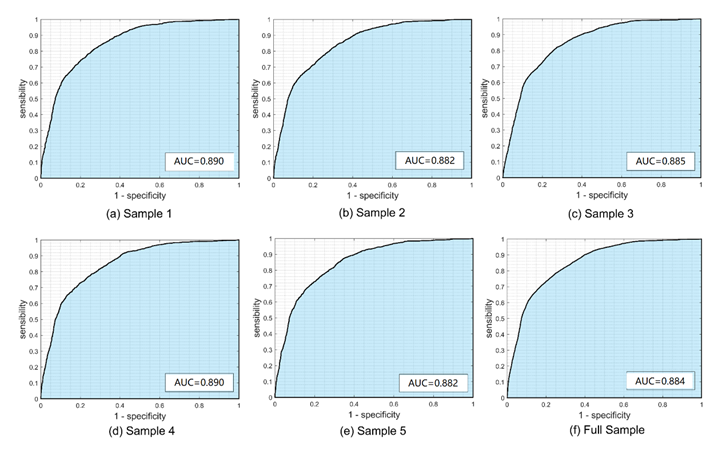
Fig. 5 Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve, (a) Sample 1, (b) Sample 2, (c) Sample 3, (d), Sample 4, (e) Sample 5, (f)Full Sample.
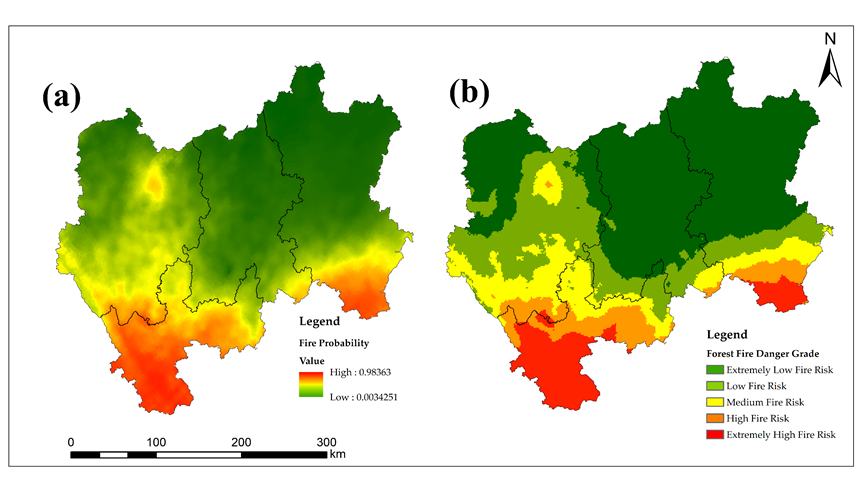
Fig. 6 Spatial pattern of susceptibility of Central Yunnan Province (CYP) (a) probability of forest wildfire, (b) forest wildfire risk grade.
该论文得到了王金亮教授主持的国家重点研发计划政府间国际科技创新合作重点专项:用地理空间技术监测和评估土地利用/土地覆被变化对区域生态安全的影响(2018YFE0184300),云南省高校高原山地资源环境遥感监测与评估科技创新团队(IRTSTYN),俄罗斯基础研究基金(19-55-80010\19),南非国家研究基金(120456)和国家自然科学基金 (41561048)的资助。
这是兰永翠同学读硕士研究生以来发表的首篇 SCI/SCIE 学术论文,是她的硕士期间发表的首篇学术论文(详见录 1、2),也是王金亮教授导师团队 2022年的发表第12篇 SCI/SCIE 论文(详见录 3),让我们恭喜兰永翠同学!希望她再接再厉!也热烈祝贺团队取好成绩!
附录 1 论文相关信息
标题:Spatial pattern prediction of forest wildfire susceptibility in Central Yunnan Province, China based on multivariate data
作者:Yongcui Lan1,2,3 , Jinliang Wang1,2,3 , Wenying Hu1 ,2,3 , Eldar Kurbanov 4 , Janine Cole5 , Jinming Sha6 , Yuanmei Jiao1,2,3 , Jingchun Zhou1,2,3
通讯作者:Jinliang Wang
作者单位:
1 Faculty of Geography, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, Yunnan, China;
2 Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing for Universities in Yunnan, Kunming, Yunnan 650500, China;
3 Center for Geospatial Information Engineering and Technology of Yunnan Province, Kunming, Yunnan, China;
4 Center for Sustainable Forest Management and Remote Sensing, Volga State University of Technology, Yoshkar-Ola, 424000, Russia;
5 Council for Geoscience, Pretoria 0001, South Africa;
6 School of Geographical Sciences, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350007, China
出版物: Natural Hazards
摘要:Wildfires are an important disturbance factor in forest ecosystems. Assessing the probability of forest wildfires can assist in forest wildfire prevention, control, and supervision. The logistic regression model is widely used to forecast the probability, spatial patterns, and drivers of forest wildfires. This study used logistic regression to establish a spatial prediction model for forest wildfire susceptibility, which was applied to evaluate the risk of forest wildfires in Central Yunnan Province (CYP), China. A forest wildfire risk classification was implemented for CYP using forest burn scar data for 2001 to 2020 and the logistic spatial prediction model for forest wildfire susceptibility. Climate, vegetation, topographical, human activities, and location were selected as forest wildfire prediction variables. The results showed that: (1) The distributions of temperature, vegetation coverage, distance to water bodies, distance to roads, and precipitation were positively correlated with the occurrence of forest wildfires. Elevation, relative humidity, the global vegetation moisture index, wind speed, slope, latitude, and distance to residential areas were negatively correlated with the occurrence of forest wildfires. (2) The results of the logistic spatial prediction model for forest wildfire susceptibility showed a good fit to wildfire data, with an overall simulation probability of 81.6%. The optimal threshold for spatial prediction for forest wildfire susceptibility in CYP was determined to be 0.414. A significance level of a selected model variable of < 0.05 resulted in an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.882-0.890. (3) Forest wildfire prevention efforts should focus on Southwest Yuxi City and southern Qujing City accounted for a high proportion of the areas at high risk of forest wildfires. Other localities should adjust forest wildfire prevention measures according to local conditions and strengthen existing wildfire prevention and emergency resource planning and allocation. (4) Some factors contributing to forest wildfires where different among the different areas. Forest wildfire risk factors had different degrees of impact under different spatial and temporal scales. The spatial relationships between wildfire disasters and influencing factors should be established in areas with heterogeneous environmental conditions for the selection of relevant factors.
关键字:Central Yunnan Province; forest wildfire; driving factors; logistic regression; susceptibility; risk grade
附录2 兰永翠同学发表SCI论文清单
自2021年9月攻读硕士至今,兰永翠同学在王金亮教授指导下发表了1篇SCI学术论文,信息如下:
[1] Yongcui Lan, Jinliang Wang*, Wenying Hu, Eldar Kurbanov, Janine Cole, Jinming Sha, Yuanmei Jiao, Jingchun Zhou. Spatial pattern prediction of forest wildfire susceptibility in Central Yunnan Province, China based on multivariate data[J]. Natural Hazard, 2022, Online. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05689-x. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月最新基础版三区,升级版三区,2021年IF 3.158)
附录 3 王金亮团队 2022 年 1 月至目前发表论文清单
自2022年1月至10月28日,王金亮教授团队发表学术论文15篇,其中12篇SCI/SCIE 论文、3篇CSCD论文,具体信息如下:
[15] Yongcui Lan, Jinliang Wang*, Wenying Hu, Eldar Kurbanov, Janine Cole, Jinming Sha, Yuanmei Jiao, Jingchun Zhou. Spatial pattern prediction of forest wildfire susceptibility in Central Yunnan Province, China based on multivariate data[J]. Natural Hazards, 2022, Online. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05689-x. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月最新基础版三区,升级版三区,2021年IF 3.158)
[14] Jiya Pan , Cheng Wang, Jinliang Wang * , Fan Gao, Qianwei Liu , Jianpeng Zhang, and Yuncheng Deng. Land Cover Classification Using ICESat-2 Photon Counting Data and Landsat 8 OLI Data: A Case Study in Yunnan Province, China[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2022.3209725. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版三区,升级版二区,2021年IF 5.343)
[13] Suling He, Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, and Fang Liu. Evaluation and analysis of upscaling of different Land Use /Land Cover products (FORM-GLC30, GLC_FCS30, CCI_LC, MCD12Q1 and CNLUCC): a case study in China[J]. Geocarto International, 2022. DOI: 10.1080/10106049.2022.2127926. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版二区,升级 版,2021年IF 4.889)
[12]Juncheng Shi, Cheng Wang, Jinliang Wang*, Xiaohuan Xi*, Xuebo Yang, and Xue Ding*. Study on the LAI and FPAR inversion of maize from airborne LiDAR and hyperspectral data[J] INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF REMOTE SENSING 2022, VOL. 43, NO. 13, 4793-4809 HTTPS://DOI.ORG/10.1080/01431161.2022.2121187. (中科院SCI期刊分区: 2021年12月最新基础版三区,升级版三区;2021年IF 3.531)
[11] Chen Y, Wang J*, Kurbanov E, Thomas A, Sha J, Jiao Y, et al. Ecological security assessment at different spatial scales in central Yunnan Province, China[J]. PLoS ONE, 2022, 17(6): e0270267. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0270267. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版三区,升级版三区;2022年最新IF 3.752)
[10] Jiya Pan, Jinliang Wang*, Fan Gao, and Guangjie Liu. Quantitative estimation and influencing factors of ecosystem soil conservation in Shangri-La, China[J]. Geocarto International, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2091160. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版二区,升级版三区;2021年IF 4.889)
[9] Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang*, Feng Cheng, Weifeng Ma, Qianwei Liu, Guangjie Liu. Natural forest ALS-TLS point cloud data registration without control points[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 2022, Online. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-022-01499-w. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021 年12月基础版SCIE二区,升级版SCIE二区;2021年IF 2.149)
[8] PAN, J. Y. ,WANG, J. L.* , LIU, G. J. ,GAO, F. Estimation of ecological asset values in Shangri_la based on remotely sensed data [J]. Applied ecology and environmental research, 2022, 20(4):2879-2895. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15666/aeer/2004_28792895 . (中科院SCI 期刊分区:2021年12月基础版SCIE四区,升级版SCIE四区;2020-2021最新IF: 0.711)
[7]Jie Li, Suling He, Jinliang Wang*, Weifeng Ma, Hui Ye. Investigating the spatiotemporal changes and driving factors of nighttime light patterns in RCEP Countries based on remote sensed satellite images [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 131944. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.jclepro.2022.131944. (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版SCIE一区,升级版 SCIE一区;Top:是;2020-2021最新IF: 9.297)
[6]何苏玲,王金亮*,角媛梅,周京春,农兰萍,朱泓.国土空间规划视角下资源环境承载力评价分析——以昆明市为例[J], 中国农业资源与区划, 2021,43(4): 119-127. DOI: 10.7621 /CJARRP. 1005-9121. 20220413 (CSCD核心库; CSSCI)
[5]潘继亚, 王金亮, 高帆. 滇西北高山峡谷典型区土地利用变化与生态安全评价 研究 [J]. 生态科学, 2022, 41(2): 29–40. (CSCD扩展库,北大核心)
[4] Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, Jun Zhang, Chenli Liu, Suling He, Lanfang Liu. Growing-season vegetation coverage patterns and driving factors in the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor based on Google Earth Engine and geographic detector [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 136, 108620. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108620. (中科院 SCI 期刊分区:2021年12 月基础版 SCIE二区,升级版SCIE二区;2022最新IF: 6.263)
[3]农兰萍,王金亮,玉院和.基于地理加权回归模型和不同植被特征参数的 TRMM 3B43 降尺度研究——以云南省为例[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(01): 99-110+117. DOI:10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2022.01.011. ( CSCD 核心库)
[2] Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang*, Pinliang Dong, Weifeng Ma, Yicheng Liu, Qianwei Liu, Zhiyan Zhang. Tree stem extraction from TLS point-cloud data of natural forests based on geometric features and DBSCAN[J]. Geocarto International, Published online: 08 Feb 2022. DOI: 10.1080/10106049.2022.2034988 (中科院SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版SCIE区,升级版SCIE三区;2021年IF 4.889)
[1] Yuanhe Yu, Xingqi Sun, Jinliang Wang*, Jianpeng Zhang. Using InVEST to evaluate water yield services in Shangri-La, Northwestern Yunnan, China[J]. Peer J, 2022, online. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12804 (中科院 SCI期刊分区:2021年12月基础版SCIE三区,升级版SCIE三区;2020-2021年IF: 2.984)
(供稿:云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室)
地址:云南省昆明市呈贡区云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院413
邮箱:ynnurs@163.com 电话:0871-65941202 技术支持:蓝队云
版权所有:Copyright © 2016-2018 云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室. All Rights Reserved