王金亮导师团队学术论文在SCIE一区(Top)期刊Journal of Cleaner Production上线发表
2022年4月29日,以李杰(云南师范大学地理学部地图学与地理信息系统专业2020级博士研究生)为第一作者,王金亮教授为通讯作者所撰写的题为“Investigating the spatiotemporal changes and driving factors of nighttime light patterns in RCEP Countries based on remote sensed satellite images”的学术论文在SCI/SCIE期刊Journal of Cleaner Production上线发表(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131944)。
2020年11月签署的《区域全面经济伙伴关系协定》(Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership,RCEP)是世界上最大、最具潜力的自由贸易区。它于2022年1月1日正式实施,该协议一经签署便引起了全世界的热切关注。RCEP协议倡导发展低碳经济,但缺乏有效的社会经济状况和碳排放监测方法。夜间灯光(Nighttime light, NTL)图像可以客观反映社会经济状况和碳排放潜力。然而,大多数研究只关注多源NTL数据的一致性校正,尽管有多种全球尺度的NTL产品,却没有深入分析NTL时空变化趋势,这也影响了Nighttime light的应用价值。鉴于此,有必要对RCEP地区的NTL动态及其驱动因素进行深入分析,这将有力促进RCEP国家低碳经济的战略部署。我们发现:(1)从2000年到2018年,RCEP区域的NTL呈亮化趋势,2018年的NTL总量是2000年的3.27倍。除日本外,所有国家的NTL都呈现出不同程度的增长趋势,这种趋势在发展中国家更为明显。增长量和增长率最大值分别出现在中国和越南。(2)夜间灯光呈上升趋势的区域占NTL区域(19年平均NTL>0的区域)的76.67%,而预测未来更明亮的区域占63.87%,这些地区通常集中在发达的城市地区,然而,大多数日本城市都观察到了暗化趋势。(3)在RECP地区,NTL与所有社会经济因素之间的关系等级大于0.6,建设用地扩张是最直接、最深刻的驱动力。与发达国家相比,发展中国家的NTL与社会经济因素的关系更为密切。
研究主要创新点和贡献:(1)利用遥感和统计学等多学科技术,研究RCEP地区和成员国过去和未来夜间灯光的时空变化,形成跨学科的方法体系,填补RCEP地区夜光变化的研究空白,推动夜间灯光时间序列产品在广度(应用)和深度(研究方法)上的拓展;此外,该研究框架还可以应用于世界其他地区夜间灯光的相关研究中。(2)揭示了影响夜光变化的主要因素,为区域经济协调发展和RCEP国家低碳战略部署提供创新性理论依据。
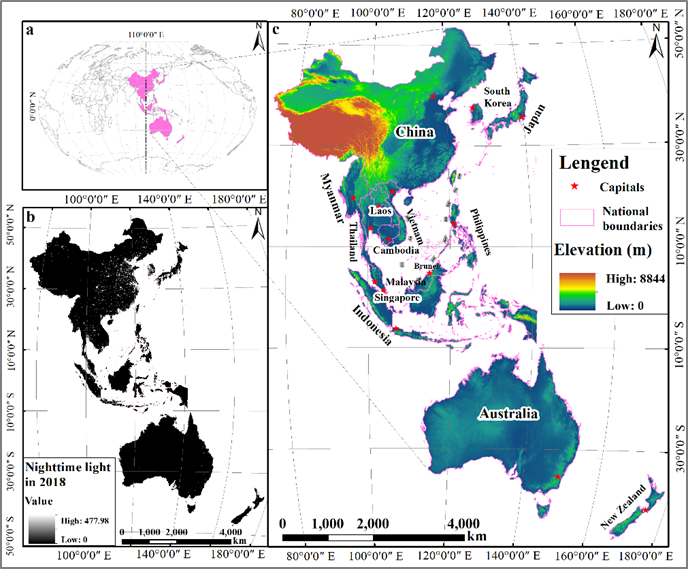
Fig. 1. Regional comprehensive economic partnership (RCEP) region: (a) position; (b) nighttime light (NTL) image in 2018; (c) member countries and elevation.
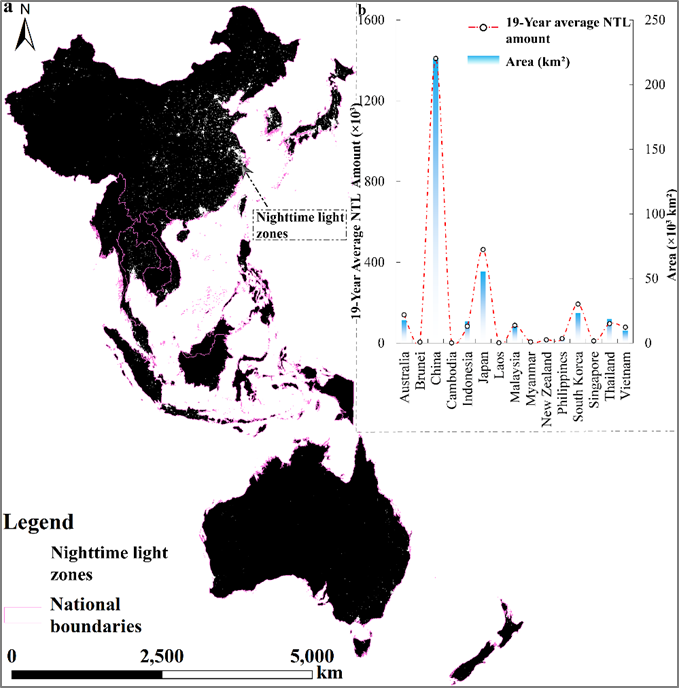
Fig. 2. The NTL zone of the RCEP region: (a) spatial pattern, (b) 19-year average NTL amount.
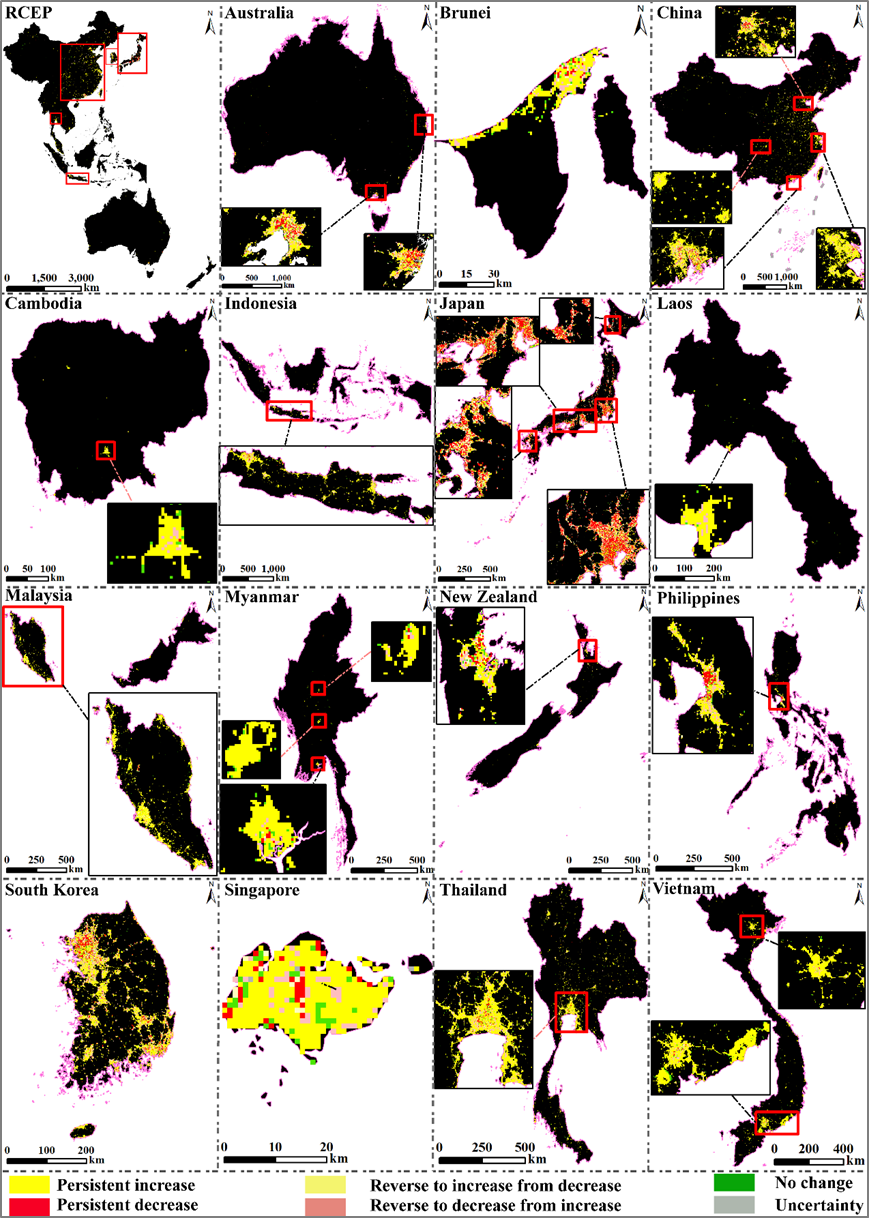
Fig. 3. Future trends in NTL in the RCEP and member countries.
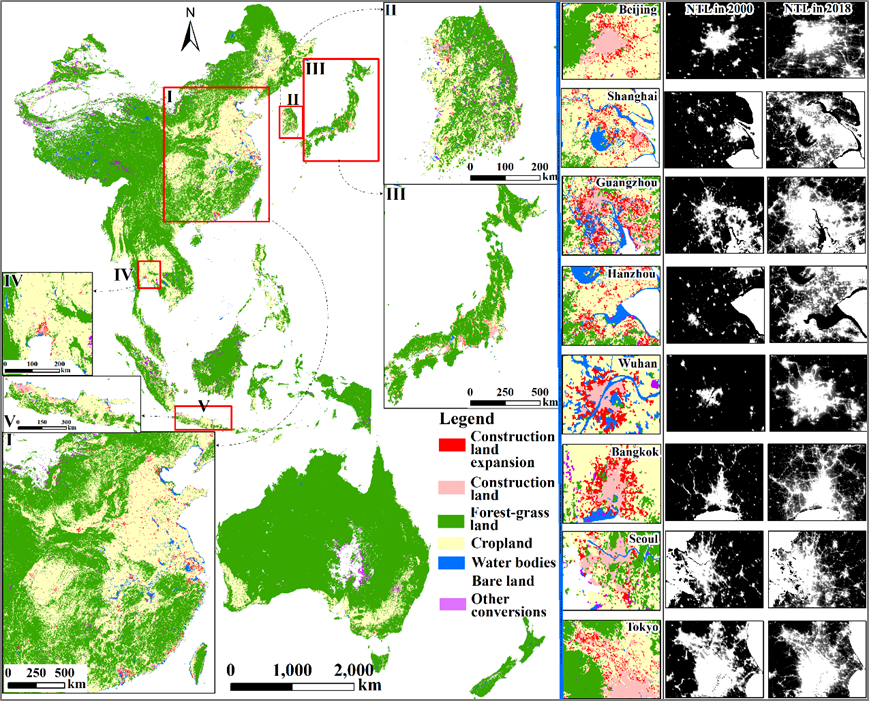
Fig. 4. Land use change in the RCEP region from 2000 to 2018.
该论文得到了王金亮教授主持的国家重点研发计划政府间国际科技创新合作重点专项:用地理空间技术监测和评估土地利用/土地覆被变化对区域生态安全的影响(2018YFE0184300),云南省教育厅科研基金项目(2022Y186);云南省青年学术技术带头人项目(2008PY056);以及云南省高校高原山地资源环境遥感监测与评估科技创新团队(IRTSTYN)的资助。
论文相关信息
标题:Investigating the spatiotemporal changes and driving factors of nighttime light patterns in RCEP Countries based on remote sensed satellite images
作者:Jie Li a,b,c, Suling He a,b,c, Jinliang Wang a,b,c,*, Weifeng Ma a,b,c, Hui Ye a,b,c
通讯作者:Jinliang Wang
作者单位:
a. Faculty of Geography, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, China; lijie2977810@163.com
b Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing for Universities in Yunnan, Kunming 650500, China
c Center for Geospatial Information Engineering and Technology of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650500, China
出版物:Journal of Cleaner Production (SCIE 一区Top, 2020-2021最新IF: 9.297)
摘要:The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) agreement signed in November 2020 is the world's largest and greatest potential free trade area. It was officially enforced on January 1, 2022, which attracted great worldwide attention. The RCEP advocates for the development of the low-carbon economy but lacks effective monitoring methods for socioeconomic conditions and carbon emissions. Nighttime light (NTL) images can objectively reflect socioeconomic status and carbon emission potential. However, most studies focused only on consistency correction for multi-source NTL data without deeply analyzing NTL dynamics. An in-depth analysis of the NTL change in the RCEP region is necessary and will strongly facilitate the strategic deployment of a low-carbon economy in RCEP countries. Sen's slope estimator, the Mann-Kendall trend test, the Mann-Kendall mutation test, and Hurst analysis were adopted to analyze the spatiotemporal changes of NTL in the past and future, and gray relational analysis was applied to explore driving factors. The results showed that (1) RCEP's NTL became brighter from 2000 to 2018, and the total NTL amount in 2018 was 3.27 times that in 2000. NTL in all countries except Japan showed an increasing trend to varying degrees, and this trend was more pronounced in developing countries. The maximum increase amount and growth rate were in China and Vietnam, respectively. (2) Areas where NTL showed an increasing trend in the past accounted for 76.67% of the NTL zones, and the areas where predicted to be brighter in the future accounted for 63.87%. These regions were generally clustered in developed urban zones. However, most Japanese cities have observed darkening trends. (3) The relational grade between NTL and all socioeconomic factors in the RECP region was greater than 0.6, and construction land expansion was the most direct and profound driver. Compared with that in developed countries, NTL in developing countries was more closely related to socioeconomic factors.
关键字:Nighttime light (NTL); carbon emission; Mann-Kendall test; Hurst analysis; the regional comprehensive economic partnership (RCEP)
附录1 李杰同学博士期间发表SCI论文清单
自2020年9月攻读博士至今,李杰在王金亮教授指导下共发表了3篇SCI学术论文,信息如下:
[3] Jie Li, Suling He, Jinliang Wang*, Weifeng Ma, Hui Ye. Investigating the spatiotemporal changes and driving factors of nighttime light patterns in RCEP Countries based on remote sensed satellite images [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 131944. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131944 . (SCIE 一区 Top,2020-2021最新IF: 9.297)
[2] Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, Jun Zhang, Chenli Liu, Suling He, Lanfang Liu. Growing-season vegetation coverage patterns and driving factors in the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor based on Google Earth Engine and geographic detector [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 136, 108620. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108620. (SCIE 二区,2020-2021最新IF: 4.958)
[1] Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, Jun Zhang, Jianpeng Zhang, Han Kong. Dynamic changes of vegetation coverage in China-Myanmar economic corridor over the past 20 years [J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2021, 102, 102378. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2021.102378. (SCIE Top,2020-2021最新IF 5.933)
附录2 王金亮团队2022年1月至目前发表论文清单
[6]Jie Li, Suling He, Jinliang Wang*, Weifeng Ma, Hui Ye. Investigating the spatiotemporal changes and driving factors of nighttime light patterns in RCEP Countries based on remote sensed satellite images [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 131944. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.jclepro.2022.131944. (SCIE,一区,Top,2020-2021最新IF: 9.297)
[5]潘继亚, 王金亮, 高帆. 滇西北高山峡谷典型区土地利用变化与生态安全评价研究[J]. 生态科学, 2022, 41(2): 29–40. (北大核心, CSCD扩展库)
[4] Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, Jun Zhang, Chenli Liu, Suling He, Lanfang Liu. Growing-season vegetation coverage patterns and driving factors in the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor based on Google Earth Engine and geographic detector [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 136, 108620. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108620. (SCIE,二区,2020-2021最新IF: 4.958)
[3]农兰萍,王金亮,玉院和.基于地理加权回归模型和不同植被特征参数的TRMM 3B43降尺度研究——以云南省为例[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(01): 99-110+117. DOI:10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2022.01.011. ( CSCD核心库)
[2] Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang*, Pinliang Dong, Weifeng Ma, Yicheng Liu, Qianwei Liu, Zhiyan Zhang. Tree stem extraction from TLS point-cloud data of natural forests based on geometric features and DBSCAN[J]. Geocarto International, Published online: 08 Feb 2022. DOI: 10.1080/10106049.2022.2034988
[1] Yuanhe Yu, Xingqi Sun, Jinliang Wang*, Jianpeng Zhang. Using InVEST to evaluate water yield services in Shangri-La, Northwestern Yunnan, China[J]. PeerJ, 2022, online. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12804 (SCIE,三区,2020-2021年IF: 2.984)
地址:云南省昆明市呈贡区云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院413
邮箱:ynnurs@163.com 电话:0871-65941202 技术支持:蓝队云
版权所有:Copyright © 2016-2018 云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室. All Rights Reserved