王金亮导师团队论文在SCIE二区期刊Ecological Indicators上线发表
2022年2月5日,以李杰(云南师范大学地理学部地图学与地理信息系统专业2020级博士研究生)为第一作者,王金亮教授为通讯作者所撰写的题为“Growing-season vegetation coverage patterns and driving factors in the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor based on Google Earth Engine and geographic detector”的学术论文在SCI/SCIE二区期刊Ecological Indicators上线发表(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108620)。
中缅经济走廊位于东南亚,是“一带一路”倡议的重点项目,一直受到国际社会的广泛关注。2020年,走廊从规划过渡到实际建设,这可能会影响当地的生态系统健康。之前的研究表明中缅经济走廊的建设导致了严重的森林砍伐,但很少有研究监测走廊区域的长期植被动态。近年来大量研究监测到全球范围内不同尺度的植被绿化趋势,但没有进一步探讨这些趋势是由于自然植被恢复还是人工作物的大规模种植。在此背景下,我们率先使用跨学科方法,如遥感动态监测、趋势分析、以及地理探测器等方法,对中缅经济走廊沿线生长季植被覆盖率(FVC)的时空格局(空间分布和变化趋势)和驱动因素进行定量分析。此外,我们还利用GEE平台的随机森林土地利用分类技术区分不同地物,以进一步提取自然植被和农作物,改善了以往大多数研究混淆自然植被和人工植被对宏观植被变化贡献量的缺点,从而更客观地分析了植被覆盖状况。我们发现,从2001年到2020年,研究区生长季的FVC整体呈增加趋势,与之相反的是,森林和草原等天然植被减少了0.68%,农田绿化是FVC增加的主要原因;基于不同子区域的独特背景,各驱动因子与FVC之间的相互作用具有显著的空间异质性。值得注意的是,农业活动导致的农田绿化抵消了自然植被的减少,并进一步促进了植被覆盖率的增加,有必要重视所监测到的自然植被退化问题。研究结果可为走廊区域的植被保护和合理布局提供科学依据。
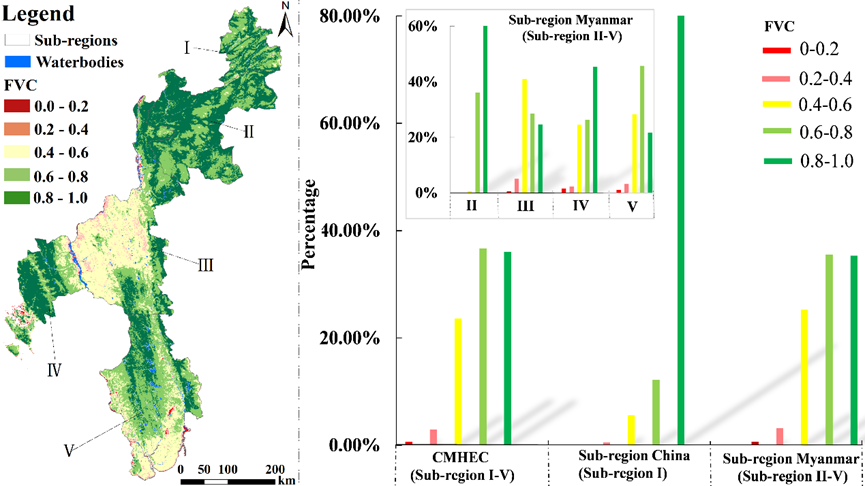
Figure 1. (a) The spatial distribution of the 20-year average FVC which was divided into five levels; (b) the proportion of FVC levels in the total area of the corresponding sub-regions.
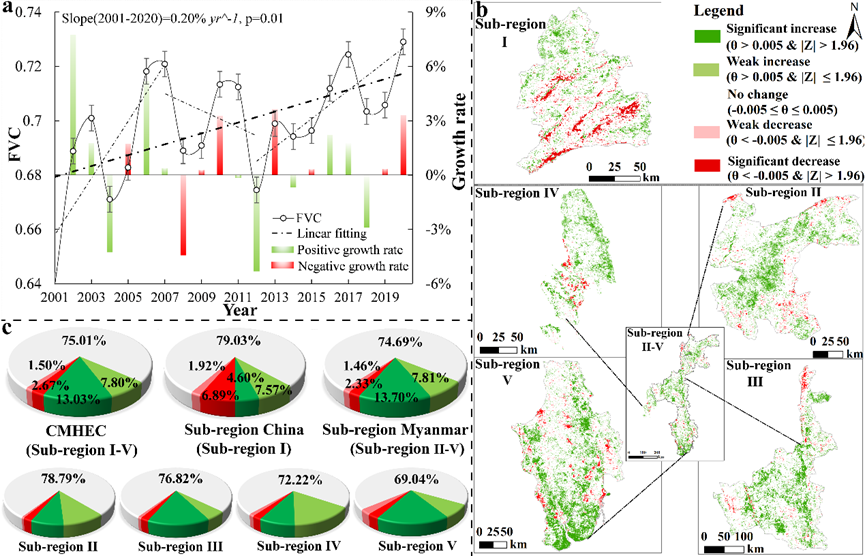
Figure 2. Changes in growing-season FVC from 2001 to 2020 (a, interannual changes; b, spatial changes; c, proportion of different change levels in the total area of the corresponding sub-regions).
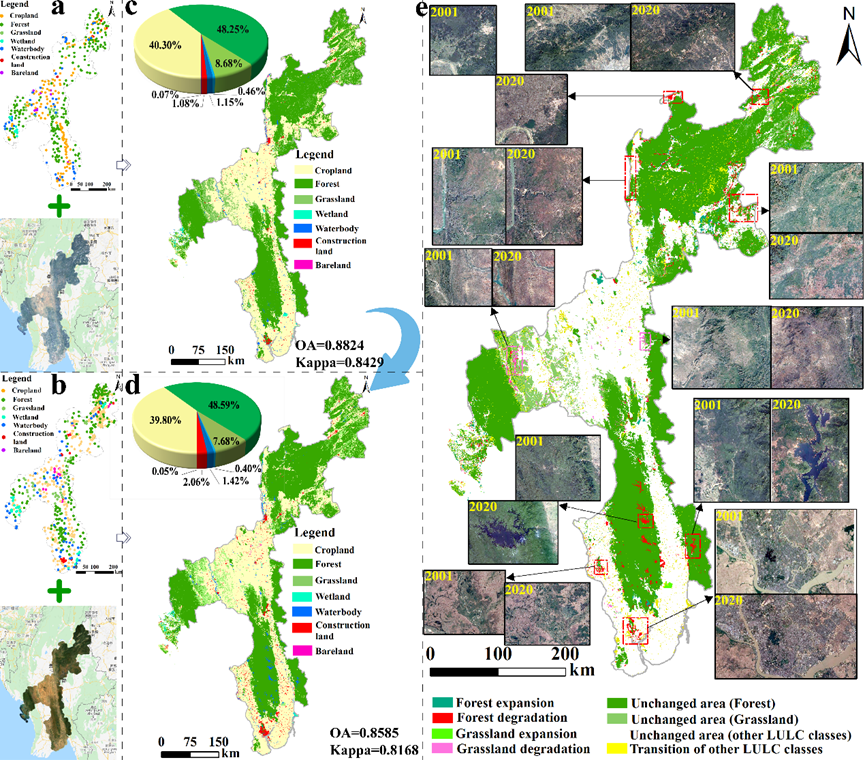
Figure 3. LULC samples and Landsat images in (a) 2001 and (b) 2020; LULC classification results and proportion of each LULC type in the total area in (c) 2001 and (d) 2020; (e) LULC transfer map in the CMEC from 2001 to 2020.
该论文得到了王金亮教授主持的国家重点研发计划政府间国际科技创新合作重点专项:用地理空间技术监测和评估土地利用/土地覆被变化对区域生态安全的影响(2018YFE0184300),云南省高校高原山地资源环境遥感监测与评估科技创新团队(IRTSTYN),俄罗斯基础研究基金(19-55-80010\19),南非国家研究基金(120456)的资助。
这是王金亮教授导师团队2022年的第三篇SCIE论文,是李杰同学发表的第二篇SCIE学术论文(录1、附录2),让我们恭喜李杰同学!希望他再接再厉!也热烈祝贺团队取得好成绩!
论文相关信息
标题:Growing-Season Vegetation Coverage Patterns and Driving Factors in the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor Based on Google Earth Engine and Geographic Detector
作者:Jie Li a,b,c, Jinliang Wang a,b,c,*, Jun Zhang d, Chenli Liu e, Suling He a,b,c, Lanfang Liu a,b,c
通讯作者:Jinliang Wang
作者单位:
a.Faculty of Geography, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, China; lijie2977810@163.com;
b Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing for Universities in Yunnan, Kunming 650500, China;
c Center for Geospatial Information Engineering and Technology of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650500, China;
d School of Earth Science, Yunnan University, Kunming 650504;
e State Key Laboratory of Grassland Agro-Ecosystems, College of Pastoral Agriculture Science and Technology, Lanzhou University 730000, China.
出版物:Ecological Indicators (2021年12月最新基础版:二区,2021年12月最新升级版:二区,2022年最新IF:4.958)
摘要:Although previous studies have shown that the construction of the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor (CMEC) has caused critical deforestation, few studies have monitored the long-term vegetation dynamics in corridor regions. Recent studies have revealed vegetation greening trends at different scales but have failed to further explore whether these trends are due to the restoration of natural vegetation or the large-scale planting of artificial crops. To investigate the vegetation dynamics and influencing factors during the growing season between 2001 and 2020 in the CMEC area, trend analysis, the random forest (RF) classifier at Google Earth Engine platform, and the geographic detector were employed to quantitatively analyze the patterns of distribution and change in vegetation coverage and its driving factors. Note that we distinguished between natural vegetation areas and artificial crop areas using the RF classification algorithm in an attempt to improve the drawback that most previous studies confused the contribution of natural vegetation and artificial vegetation to macro vegetation change. We discovered that (1) the growing-season average fractional vegetation cover (FVC) was 0.7033, which was relatively low in central and southern regions. The FVC increased by 0.21% yr-1 from 2001 to 2020, and areas with an increasing trend in FVC were 16.67% more than those with a decreasing trend. (2) Although forests and grasslands were reduced by 0.68%, the cropland that prominently clustered in the central and southern regions contributed 50.37% to an increase in FVC, and the decreasing effects on natural vegetation were offset by the increase in artificial crops. (4) The factors that influence FVC distribution were ranked in descending order: land use/land cover (LULC) > climate > topography > anthropogenic activity; factors that influence FVC change were ranked as: anthropogenic activity > climate > LUCC. Note that the grain yield influence on the FVC distribution increased 0.31% yr -1, which was also the most important factor driving FVC change, indicating that agricultural activities increasingly facilitated vegetation greening.
关键字:Fractional vegetation cover (FVC); Random forest; Google Earth Engine; Geographic detector; Land use/land cover (LULC).
附录1 李杰同学发表SCI论文清单
自2020年9月攻读博士至今,李杰在王金亮教授指导下共发表了2篇SCI学术论文,信息如下:
[2] Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, Jun Zhang, Chenli Liu, Suling He, Lanfang Liu. Growing-season vegetation coverage patterns and driving factors in the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor based on Google Earth Engine and geographic detector [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 136, 108620. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108620. (2021年12月最新基础版:环境科学与生态学二区,2021年12月最新升级版:环境科学与生态学二区,2021年IF 4.958)
[1] Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, Jun Zhang, Jianpeng Zhang, Han Kong. Dynamic changes of vegetation coverage in China-Myanmar economic corridor over the past 20 years [J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2021, 102, 102378. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2021.102378. (2021年12月最新基础版:地学一区,2021年12月最新升级版:地球科学一区,2021年IF 5.933)
附录2 王金亮教授导师团队2022年发表SCIE论文清单
自2022年1月至今,王金亮教授导师团队共发表了3篇SCIE学术论文,信息如下:
[3] Jie Li, Jinliang Wang*, Jun Zhang, Chenli Liu, Suling He, Lanfang Liu. Growing-season vegetation coverage patterns and driving factors in the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor based on Google Earth Engine and geographic detector [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 136, 108620. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108620. (2021年12月最新基础版:环境科学与生态学二区,2021年12月最新升级版:环境科学与生态学二区,2021年IF 4.958)
[2] Jianpeng Zhang, Jinliang Wang*, Pinliang Dong, Weifeng Ma, Yicheng Liu, Qianwei Liu, Zhiyan Zhang. Tree stem extraction from TLS point-cloud data of natural forests based on geometric features and DBSCAN[J]. Geocarto International, posted online: 26 Jan 2022 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2034988. (2021年12月基础版二区,2021年12月升级版三区,2021年IF 4.889)
[1] Yuanhe Yu, Xingqi Sun, Jinliang Wang. Using InVEST to evaluate water yield services in Shangri-La, Northwestern Yunnan, China[J]. Peer J10: e12804, Online: January 14, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12804.(2021年12月基础版SCIE三区,2021年12月升级版SCIE三区, 2021年2.984)
地址:云南省昆明市呈贡区云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院413
邮箱:ynnurs@163.com 电话:0871-65941202 技术支持:蓝队云
版权所有:Copyright © 2016-2018 云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室. All Rights Reserved