王金亮导师研究小组论文在SCIE期刊PeerJ上线发表
2022年1月14日,以玉院和(云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院地图学与地理信息系统专业2017级硕士研究生,现为南京师范大学地理科学学院地图学与地理信息系统专业2020级博士研究生)为第一作者,王金亮教授为通讯作者撰写题为“Using InVEST to evaluate water yield services in Shangri-La, Northwestern Yunnan, China”论文在SCI/SCIE期刊PeerJ(三区,2020年IF 2.98)上线发表(https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12804)。
产水量是一项重要的生态系统服务,直接关系到人类福祉,影响到社会经济和生态系统的可持续发展。以香格里拉市为研究区,采用年均降水量数据、潜在蒸散量数据、植物可利用含水量、土壤深度数据、生物物理量参数、Zhang系数和土地覆盖数据,基于InVEST模型分析香格里拉市1974-2015年产水量的时空特征并划分产水量重要性等级,探讨气候、地形、土地利用方式对产水生态系统服务功能的影响。研究采用的模型参数可为类似气候条件下地区的相关研究提供参考。
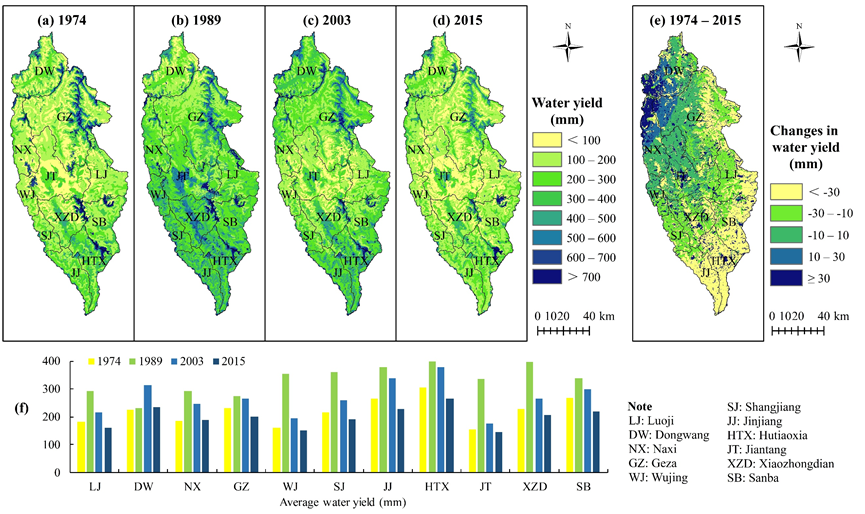
Fig. 1. A summary of water yield for Shangri-La City, Yunnan Province, China as simulated by the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Service Tradeoffs (InVEST) model. The spatial distribution of water yield for different years is shown in (a), (b), (c), and (d), whereas (e) shows the spatial distribution of the change in water yield between 1974 and 2015. A statistical summary of average water yield for different areas and different years is shown in (f).
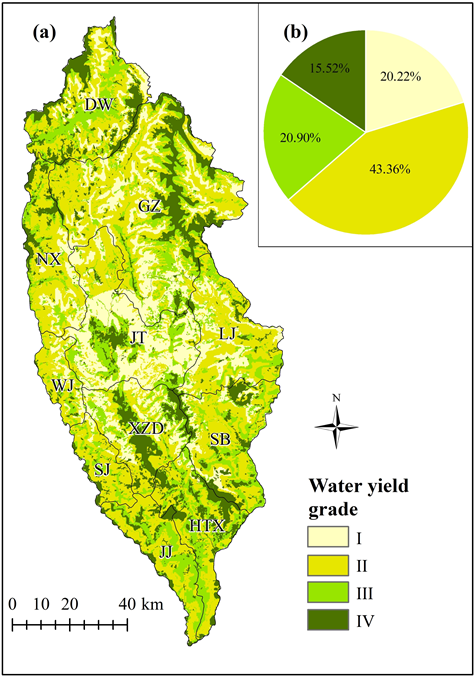
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of water yield in Shangri-La City, Yunnan Province, China as simulated by the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Service Tradeoffs (InVEST) model. (a) according to Grades I–IV indicating the importance of the water yield ecosystem service, (b) the area proportion of each grade in 2015.
该论文得到了王金亮教授主持的国家自然基金项目:联合ULS与TLS点云数据的滇西北天然林单木生物量估算研究(41961060)、国家重点研发计划政府间国际科技创新合作重点专项:用地理空间技术监测和评估土地利用/土地覆被变化对区域生态安全的影响(2018YFE0184300)和云南省高校高原山地资源环境遥感监测与评估科技创新团队(IRTSTYN)的资助。
这是王金亮教授导师团队2022年的第一篇论文,是玉院和同学发表的第7篇SCIE学术论文(详见录1),让我们恭喜玉院和同学!希望再接再厉!也热烈祝贺团队取得好成绩!
论文相关信息
标题:Using InVEST to evaluate water yield services in Shangri-La, Northwestern Yunnan, China
作者:Yuanhe Yu1,2, Xingqi Sun3, Jinliang Wang1 and Jianpeng Zhang1
通讯作者:Jinliang Wang
作者单位:
1 Faculty of Geography, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, China;
2 School of Geography, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, China;
3 The First Geodetic Surveying Brigade of MNR, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China.
出版物:Peer J
摘要:Water yield is an ecosystem service that is vital to not only human life, but also sustainable development of the social economy and ecosystem. This study used annual average precipitation, potential evapotranspiration, plant available water content, soil depth, biophysical parameters, Zhang parameter, and land use/land cover (LULC) as input data for the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Service Tradeoffs (InVEST) model to estimate the water yield of Shangri-La City from 1974 to 2015. The spatiotemporal variations and associated factors (precipitation, evapotranspiration, LULC, and topographic factors) in water yield ecosystem services were then analyzed. The result showed that: (1) The water yield of Shangri-La City decreases from north and south to the center and showed a temporal trend from 1974 to 2015 of an initial decrease followed by an increase. Areas of higher average water yield were mainly in Hutiaoxia Town, Jinjiang Town, and Shangjiang Township. (2) Areas of importance for water yield in the study area which need to be assigned priority protection were mainly concentrated in the west of Jiantang Town, in central Xiaozhongdian Town, in central Gezan Township, in northwestern Dongwang Township, and in Hutiaoxia Town. (3) Water yield was affected by precipitation, evapotranspiration, vegetation type, and topographic factors. Water yield was positively and negatively correlated with precipitation and potential evapotranspiration, respectively. The average water yield of shrubs exceeded that of meadows and forests. Terrain factors indirectly affected the ecosystem service functions of water yield by affecting precipitation and vegetation types. The model used in this study can provide references for relevant research in similar climatic conditions.
关键词:Water yield; InVEST model; Ecosystem services; Shangri-La City; Northwest Yunnan;
China
附录1 玉院和同学发表SCI论文清单
2017年9月硕士入学至今,玉院和在王金亮教授指导下发表了9篇学术论文,其中的SCI论文7篇。7篇SCI论文信息如下:
[7] Yuanhe Yu, Xingqi Sun, Jinliang Wang*, Jianpeng Zhang. Using InVEST to evaluate water yield services in Shangri-La, Northwestern Yunnan, China[J]. PeerJ, 2022, online.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12804 (SCIE三区,2020年IF: 2.98)
[6] Yuanhe Yu,Yuzhen Shen, Jinliang Wang*, Yuchun Wei, Zhiyuan Liu. Simulation and mapping of drought and soil erosion in Central Yunnan Province, China[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(11), 4556-4572.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.08.028 (SCI升级版三区, 2020年IF: 2.152)
[5] Jinliang Wang, Yuanhe Yu*. Comprehensive drought monitoring in Yunnan Province, China using multisource remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2021, 18(6):1537-1549.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6333-7 (SCIE三区, 2020 IF: 2.071)
[4] Yuanhe Yu, Yuzhen Shen, Jinliang Wang*, Yuchun Wei*, Lanping Nong, Huan Deng. Assessing the response of vegetation change to drought during 2009-2018 in Yunnan Province, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28: 47066–47082.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13835-4 (SCI/SCIE 三区, 2020年IF: 4.223)
[3] Yuanhe Yu, Jinliang Wang*, Feng Cheng, Huan Deng, Sheng Chen. Drought monitoring in Yunnan Province based on a TRMM precipitation product[J]. Natural Hazards, 2020, 104(3): 2369-2387.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04276-2 (SCI 三区, 2019年IF: 2.427)
[2] Yuanhe Yu, Jinliang Wang*, Feng Cheng, Yun Chen. Soil Moisture by Remote Sensing Retrieval in the Tropic of Cancer of Yunnan Province[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2020, 29(2): 1981-1993.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/110203 (SCI 四区, 2019年IF: 1.383)
[1] Yuanhe Yu, Jinliang Wang*, Guangjie Liu, Feng Cheng. Forest Leaf Area Index Inversion Based on Landsat OLI Data in the Shangri-La City[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2019, 47(6): 967-976.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-00950-6 (SCI 四区, 2019年IF: 0.997)
地址:云南省昆明市呈贡区云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院413
邮箱:ynnurs@163.com 电话:0871-65941202 技术支持:蓝队云
版权所有:Copyright © 2016-2018 云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室. All Rights Reserved