王金亮导师研究小组的论文在SCI期刊Applied Ecology and Environmental Research上发表
2020年10月13日,以云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室2016级硕士研究生刘致远为第一作者、王金亮教授为通讯作者撰写题为“Temporal and Spatial Variation of Soil Erosion in Central Yunnan Province, China”的论文在SCI期刊Applied Ecology and Environmental Research上发表(DOI: http://dx.doi.org /10.15666/aeer/1805_66916712, 文章链接:http://aloki.hu/indvol OF.htm)。论文以滇中地区为研究区,利用多时相遥感影像、GIS技术和RUSLE模型对滇中地区1980-2018年的土壤侵蚀量进行了估算。
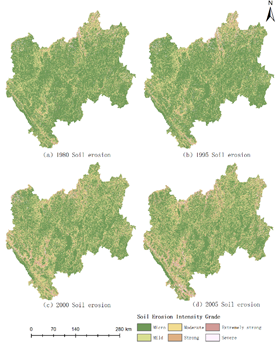
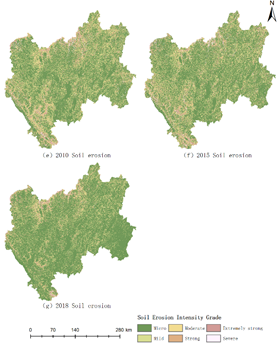
滇中地区土壤侵蚀强度的空间分布
论文得到了王金亮教授主持国家重点研发计划“利用地理空间技术监测和评估土地利用/土地覆被变化对区域生态安全的影响”(No.2018YFE0184300)、国家自然科学基金“滇中地区生态安全评价与预警研究”(No.41561048)、云南省哲学社会科学规划办公室重点项目“云南县域生态资产测量技术方法与实证研究”(No.ZDZD201506)、云南省中青年学术技术带头人(No.2008PY056)、云南省高校科技创新团队支持计划(IRTSTYN)的资助。
标题:Temporal and Spatial Variation of Soil Erosion in Central Yunnan Province, China
作者:LIU, Z. Y. – ZHANG, J. P. – WANG, J. L.
通讯作者:WANG, J. L., jlwang@ynnu.edu.cn
作者单位:1. College of Tourism and Geographic Sciences, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, China; 2. Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing, Universities in Yunnan, Kunming 650500, China; 3. Remote Sensing Research Laboratory, Center for Geospatial Information Engineering and Technology of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650500, China.
出版物:Applied Ecology and Environmental Research
2020年影响因子/JCR分区:0.712/Q4
摘要:Soil erosion is one of the major global environmental problems. Understanding the spatiotemporal changes in soil erosion is of great significance to its prevention and control of soil erosion and the optimization of ecological environments. Taking Central Yunnan Province (CYP), China as the study area, multitemporal remotely sensed images, GIS technology and the RUSLE model were used to estimate the amount of soil erosion in the CYP during 1980-2018. The results show the following: (1) During the study period, the soil erosion situation in the CYP showed a growing development trend. With 2005 as a turning point, the area of micro-erosion first decreased and then increased, and the area of soil erosion with mild and above intensity was effectively controlled. (2) Through the global spatial autocorrelation, the spatial distribution of soil erosion intensity in the CYP has significant aggregation, and the global Moran I index is between 0.48 and 0.66. The areas with moderate and above erosion intensity were mostly distributed in the mountains, northern valleys, and the northwestern and southwestern regions of the CYP. Through the analysis of local spatial autocorrelation, it is also proved that the distribution of intensity soil erosion is mostly related to regional topography.
关键字:Soil erosion, RUSLE, temporal and spatial variation, spatial autocorrelation, Moran I index
地址:云南省昆明市呈贡区云南师范大学旅游与地理科学学院413
邮箱:ynnurs@163.com 电话:0871-65941202 技术支持:蓝队云
版权所有:Copyright © 2016-2018 云南省高校资源与环境遥感重点实验室. All Rights Reserved